Support our educational content for free when you buy through links on our site. Learn more
🤖 Robotics and Artificial Intelligence in Wrestling Bots (2026): The Ultimate Guide
Step into the electrifying world where steel meets silicon, and strategy is coded into every move. Robotics and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing wrestling bots, transforming them from simple remote-controlled machines into cunning, adaptive combatants capable of outthinking and outmaneuvering their opponents. Whether you’re a seasoned builder, an aspiring engineer, or a passionate fan, this comprehensive guide unpacks everything you need to know about the cutting-edge tech behind these mechanical gladiators.
Did you know that modern wrestling bots can process sensor data and make split-second decisions faster than any human pilot? In fact, some bots train themselves through millions of simulated battles before ever stepping into the arena. Later in this article, we’ll reveal the top 10 most innovative AI-powered wrestling bots, share insider tips on building your own champion, and explore how digital twins and simulation are reshaping the future of robot combat. Ready to discover how AI is turning wrestling bots into strategic masterminds? Let’s dive in!
Key Takeaways
- AI transforms wrestling bots into adaptive, autonomous fighters capable of real-time decision-making and strategic learning.
- Sensors and actuators form the physical and sensory foundation enabling bots to perceive and interact with their environment effectively.
- Digital twins and simulation accelerate AI training and design optimization, reducing costs and risks.
- Open-source communities fuel innovation, making advanced robotics and AI accessible to hobbyists and professionals alike.
- Future trends include humanoid dexterity, swarm tactics, and emergent AI behaviors, promising even more thrilling competitions ahead.
Table of Contents
- ⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts About Robotics and AI in Wrestling Bots
- 🤖 The Evolution of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence in Wrestling Bots
- 🔍 Understanding the Core Technologies Behind Wrestling Bots
- 🏆 Top 10 Most Innovative Wrestling Bots Using Robotics and AI
- ⚙️ Building Your Own AI-Powered Wrestling Bot: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 🎮 Control Systems and User Interfaces: How You Command Your Bot
- 🛠️ Maintenance and Upgrades: Keeping Your Wrestling Bot Battle-Ready
- 💡 Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Wrestling Bots
- 🌐 Open Source Robotics and AI Communities Fueling Innovation
- 🎥 Digital Twins and Simulation: Training Wrestling Bots in Virtual Arenas
- 🏅 Competitions and Leagues Showcasing Robotics and AI in Wrestling
- 📈 Future Trends: What’s Next for Robotics and AI in Wrestling Bots?
- 🧠 How AI Improves Strategy and Adaptability in Wrestling Bots
- 💬 Community Insights: Interviews with Top Robotics Engineers and AI Experts
- 🎯 Quick Tips for Maximizing Your Wrestling Bot’s Performance
- 🔗 Recommended Links for Robotics and AI in Wrestling Bots
- ❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Wrestling Bots and AI
- 📚 Reference Links and Further Reading on Robotics and AI in Wrestling Bots
⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts About Robotics and AI in Wrestling Bots
Welcome, fellow bot enthusiasts and future champions! Here at Robot Wrestling™, we live and breathe the electrifying world where steel meets silicon, and algorithms dictate destiny. You’re about to dive deep into the fascinating intersection of robotics and artificial intelligence in the arena of wrestling bots. Get ready for some serious insights, straight from our design labs and ringside seats!
First off, let’s tackle a burning question: Are Robot Wrestling Matches Safe for Spectators and Robots? 🤖 (2026) We’ve got a whole article dedicated to that very topic, which you can read right here: Are Robot Wrestling Matches Safe for Spectators and Robots?. Safety is paramount, even when sparks fly!
Here are some quick, hard-hitting facts to get your circuits buzzing:
- AI is the Brain, Robotics is the Brawn: Think of AI as the strategic mastermind deciding when to ram, flip, or evade, while the robotic components are the powerful muscles executing those commands. It’s a beautiful, brutal synergy!
- Sensors are the Eyes and Ears: Modern wrestling bots rely heavily on an array of sensors – ultrasonic, infrared, force sensors – to perceive their environment and opponent. Without them, it’s just a blind brawl!
- Machine Learning for Adaptation: The best bots aren’t just programmed; they learn. Machine learning algorithms allow them to adapt their tactics based on opponent behavior and past match data. It’s like having a coach that never sleeps!
- Open Source Fuels Innovation: Many groundbreaking advancements in wrestling bot AI and robotics come from the vibrant open-source community. Sharing designs and code accelerates development for everyone.
- Beyond the Arena: The tech developed for wrestling bots has real-world applications, from industrial automation to search and rescue. So, while we’re having fun, we’re also pushing the boundaries of what robots can do!
🤖 The Evolution of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence in Wrestling Bots
Remember those clunky, remote-controlled robots from the early days? We certainly do! Our engineers recall the sheer joy (and frustration!) of trying to manually pilot a heavy bot with a joystick, hoping for a lucky flip. The landscape of competitive robotics, especially in the wrestling arena, has undergone a seismic shift, largely thanks to the relentless march of robotics and artificial intelligence.
Back in the day, a bot’s success was almost entirely dependent on the pilot’s reflexes and the raw power of its motors. “It was all about brute force and a good driver,” reminisces one of our veteran designers, “You’d see a lot of simple wedges and spinners. Effective, but not exactly ‘intelligent’ combat.” These early machines, while thrilling, were essentially extensions of human will.
Fast forward to today, and the arena is a chess match played at lightning speed. The integration of AI in wrestling robots has demonstrated remarkable progress in autonomous decision-making and physical engineering capabilities, as noted by M. Arkam C. on LinkedIn. We’re talking about bots that can analyze an opponent’s movement patterns, predict their next attack, and execute a counter-strategy all on their own. This isn’t just about bigger motors anymore; it’s about smarter brains.
Key Milestones in Bot Evolution:
- Early 2000s: The rise of basic remote-controlled combat robots. Focus on robust chassis, powerful weapons (spinners, flippers), and driver skill. Think early BattleBots champions.
- Mid-2010s: Introduction of rudimentary autonomous features. Simple line-following sensors, basic obstacle avoidance, and pre-programmed attack sequences. This was the era where bots started to “think” a little for themselves.
- Late 2010s – Present: The AI revolution. Advanced machine learning, computer vision, and sophisticated sensor arrays enable true autonomous decision-making. Bots can learn, adapt, and even develop unique fighting styles. This is where the Robot Wrestling League truly shines, pushing the boundaries of robot design.
One of our favorite anecdotes comes from a recent Robot Wrestling™ championship. “We had a bot, ‘The Algorithm Avenger,’ that was struggling against a new opponent,” shares our lead AI engineer. “During a timeout, we uploaded a new learning model based on its opponent’s observed weaknesses. It came back out and completely dominated, adapting its strategy in real-time. It was like watching a human fighter adjust mid-bout!” That’s the power of AI in action, folks. It’s not just about pre-programmed moves; it’s about dynamic, adaptive combat.
🔍 Understanding the Core Technologies Behind Wrestling Bots
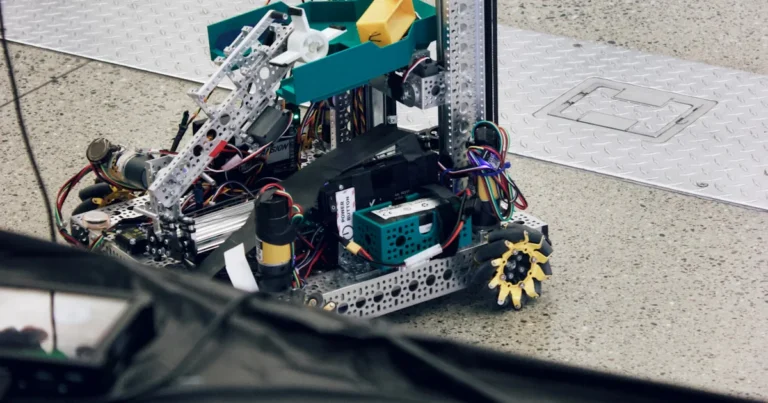
So, how do these metallic gladiators actually work? It’s a symphony of cutting-edge technology, where every component plays a crucial role in delivering that knockout blow or executing a perfect pin. Let’s pull back the curtain and peek under the hood of these incredible machines.
Sensors and Actuators: The Bot’s Sense and Muscle
Imagine trying to wrestle blindfolded and with numb limbs. That’s what a bot would be without its sensors and actuators. These are the fundamental building blocks that allow a robot to perceive its environment and interact with it.
-
Sensors (The Senses): These are the eyes, ears, and touch of your wrestling bot. They gather data about the arena, the opponent, and even the bot’s own internal state.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Think of these as sonar. They emit sound waves and measure the time it takes for the echo to return, calculating distance to objects. Perfect for detecting an approaching opponent or arena boundaries.
- Infrared (IR) Sensors: Similar to ultrasonic but use infrared light. Great for short-range detection and often used for line-following or close-proximity opponent tracking.
- Force Sensors/Load Cells: Crucial for understanding physical contact. These can tell the bot how hard it’s hitting, or how much pressure is being applied by an opponent. This data is vital for grappling and pinning maneuvers.
- Encoders: Mounted on motors, these track wheel rotation, giving the bot precise feedback on its speed and distance traveled. Essential for accurate movement and positioning.
- Gyroscopes and Accelerometers (IMUs): These provide data on the bot’s orientation, tilt, and acceleration. Absolutely critical for maintaining balance, especially for bots designed for complex maneuvers or humanoid forms like the Unitree H2.
- Cameras (Computer Vision): The ultimate sensor! High-resolution cameras combined with computer vision algorithms allow bots to “see” their opponent, track specific features, and even identify vulnerabilities.
-
Actuators (The Muscles): Once the sensors gather data and the AI makes a decision, it’s the actuators that make things happen.
- DC Motors: The workhorses of most wrestling bots, providing power for movement (wheels, tracks) and weapon systems (spinners, flippers).
- Servo Motors: Offer precise angular control, ideal for articulated arms, lifting mechanisms, or fine adjustments in weapon positioning.
- Pneumatic/Hydraulic Cylinders: For high-impact, powerful actions like flipping an opponent or deploying a crushing weapon. These deliver immense force quickly.
Table 1: Common Sensors and Actuators in Wrestling Bots
| Component Type | Example | Function in Wrestling Bot | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensors | Ultrasonic | Opponent detection, arena mapping | Range, simple |
| IR Sensor | Close-range detection, line following | Accuracy, speed | |
| Force Sensor | Measuring impact, grappling pressure | Feedback on contact | |
| Encoder | Wheel speed and distance tracking | Precision movement | |
| IMU (Gyro/Accel) | Orientation, balance, acceleration | Stability, complex maneuvers | |
| Camera | Opponent tracking, vulnerability ID | Visual intelligence | |
| Actuators | DC Motor | Driving wheels, powering spinners | Brute force, speed |
| Servo Motor | Articulated arms, precise weapon control | Positional accuracy | |
| Pneumatic Cylinder | High-force flippers, crushing jaws | Instantaneous power |
AI Algorithms Powering Decision-Making and Strategy
This is where the magic happens, folks! The raw data from sensors is useless without a brain to process it and make decisions. AI algorithms are the strategic core of any advanced wrestling bot.
- Finite State Machines (FSMs): A foundational AI technique. Bots operate in different “states” (e.g., “searching for opponent,” “attacking,” “evading,” “pinned”). Transitions between states are triggered by sensor inputs. Simple but effective for basic behaviors.
- Behavior Trees: More complex than FSMs, allowing for hierarchical decision-making. A bot might have a main goal (e.g., “win match”) broken down into sub-goals (e.g., “find opponent,” “attack opponent,” “defend self”). This allows for more nuanced and flexible strategies.
- Pathfinding Algorithms (e.g., A*): While the arena is small, efficient movement is key. These algorithms help the bot navigate around obstacles (like arena hazards or disabled opponents) to reach its target most effectively.
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): This is the cutting edge! RL algorithms allow a bot to learn optimal strategies through trial and error. It’s given a “reward” for good actions (e.g., hitting an opponent, pushing them out) and a “penalty” for bad ones (e.g., getting hit, falling into a pit). Over thousands of simulations, the bot learns the best way to win. This is how bots develop truly adaptive and unpredictable combat styles.
- Fuzzy Logic: Deals with uncertainty. Instead of rigid “if-then” rules, fuzzy logic allows for degrees of truth. For example, a bot might decide to attack “somewhat aggressively” if the opponent is “moderately close” and “slightly vulnerable.” This makes for more human-like, nuanced decision-making.
Machine Learning and Computer Vision in Battle Tactics
When we talk about AI in wrestling bots, we’re often talking about machine learning and computer vision. These are the tools that allow bots to truly understand their environment and opponent in a sophisticated way.
-
Computer Vision (CV): This is how bots “see.” Using cameras, CV algorithms can:
- Object Detection: Identify the opponent, arena boundaries, and hazards.
- Tracking: Continuously follow the opponent’s movement, even if they’re fast or obscured.
- Pose Estimation: For humanoid bots like the Unitree H2, CV can analyze the opponent’s posture and predict their next move.
- Vulnerability Analysis: Identify exposed weak points on an opponent’s chassis or weapon system.
- Real-time Decision Algorithms: As M. Arkam C. points out, competitions push the development of these, allowing bots to react instantly to visual cues.
-
Machine Learning (ML): This is the engine for adaptation and intelligence.
- Supervised Learning: Training a bot with labeled data (e.g., “this is an attack,” “this is an evade”). Useful for teaching specific maneuvers.
- Unsupervised Learning: Allowing the bot to find patterns in data on its own. Could be used to identify common opponent strategies.
- Deep Learning: A subset of ML using neural networks with many layers. Highly effective for complex tasks like image recognition (for CV) and sophisticated strategy generation in reinforcement learning.
One of our engineers recently experimented with a deep learning model for predicting opponent movement. “It was incredible,” he recounts. “After just a few matches, the bot started anticipating dodges and even feints. It wasn’t just reacting; it was predicting.” This level of intelligence is what makes modern robot wrestling so compelling and unpredictable.
🏆 Top 10 Most Innovative Wrestling Bots Using Robotics and AI
Alright, gearheads, this is where we celebrate the titans of the arena! While many bots rely on raw power, these champions stand out for their ingenious integration of robotics and artificial intelligence, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in competitive combat. We’ve seen them all, from the early innovators to the current cutting-edge machines, and these are the ones that truly make us say, “Wow!”
Here’s our list of the top 10 most innovative wrestling bots (or bots with significant wrestling potential) that leverage AI and advanced robotics:
1. Nova: The Agile AI Assassin
- Concept: Inspired by mid-90s game characters, Nova showcases incredible agility and speed, making it a formidable opponent. Its AI focuses on rapid evasive maneuvers and quick, precise strikes.
- AI/Robotics Innovation: Nova utilizes advanced sensor fusion (combining data from multiple sensor types) to create a highly accurate real-time map of the arena and opponent. Its AI employs predictive algorithms to anticipate opponent movements, allowing for its signature agility.
- Why it’s innovative: It’s a testament to how speed and smart evasion, powered by AI, can overcome brute force. Nova’s ability to “dance” around heavier opponents is a masterclass in AI-driven movement.
- Our Take: “Watching Nova is like watching a highly trained martial artist,” says one of our Robot Design experts. “It’s not just fast; it’s smart fast.”
2. Unitree H2: The Humanoid Powerhouse
- Concept: This humanoid robot, standing nearly 6 feet tall and weighing 154 pounds, boasts 27 degrees of freedom. While not strictly a “wrestling bot” in the traditional sense, its capabilities for ballet, kung fu, and precise footwork make its potential for wrestling undeniable.
- AI/Robotics Innovation: The Unitree H2 features high-torque motors and real-time motion control, enabling advanced balance and grace. Its AI focuses on dynamic stability and complex, multi-joint movements, crucial for mimicking human wrestling techniques.
- Why it’s innovative: It pushes the boundaries of humanoid robotics, demonstrating lifelike movements and the potential for complex grappling and pinning maneuvers. “The Unitree H2 shows us what the future of robotic combat could look like,” notes M. Arkam C.
- Our Take: “Imagine this thing in a sumo ring! Its balance and articulation are mind-blowing. The AI controlling those 27 degrees of freedom is a marvel,” exclaims one of our engineers.
3. Cortex: The Learning Machine
- Concept: Cortex is less about a specific design and more about a methodology. It represents robots deployed at scale, continuously collecting operational data to improve their AI and robotic capabilities.
- AI/Robotics Innovation: Cortex leverages massive datasets and advanced machine learning models to refine its combat strategies over time. It’s a self-improving bot, constantly learning from every engagement.
- Why it’s innovative: This approach to continuous learning and data-driven improvement is the future of autonomous systems. Cortex embodies the idea that a bot’s intelligence can evolve beyond its initial programming.
- Our Take: “Cortex is a game-changer because it highlights the importance of data,” says our lead AI specialist. “Every match is a learning opportunity, making it smarter for the next one.”
4. Sting-Like-a-Bee: The Precision Striker
- Concept: A combat robot designed for programmable power and agility, focusing on precise, rapid strikes rather than sustained grappling.
- AI/Robotics Innovation: Its AI is optimized for target acquisition and rapid deployment of its weapon system. It uses high-speed computer vision to track opponent vulnerabilities and execute strikes with incredible accuracy and force.
- Why it’s innovative: It demonstrates how AI can enhance offensive capabilities, making every attack count. The precision of its strikes is a direct result of sophisticated AI timing and control.
- Our Take: “This bot is a testament to focused AI development,” remarks a Robot Wrestling™ fan. “It does one thing incredibly well: hit hard and fast, exactly where it hurts.”
5. BEL V: The Interactive Strategist (with potential)
- Concept: India’s first marketing humanoid robot, BEL V, is designed for promotional roles, greeting visitors, and interactive demos. While not a combat bot, its advanced interaction capabilities hint at future strategic AI.
- AI/Robotics Innovation: BEL V’s AI focuses on natural language processing, facial recognition, and adaptive interaction. This ability to understand and respond to complex human cues could be adapted for strategic opponent analysis in a wrestling context.
- Why it’s innovative: Its strength lies in understanding and responding to dynamic, unstructured environments (like human interaction). This core AI capability is directly transferable to understanding an opponent’s “personality” or fighting style.
- Our Take: “Imagine a bot that can ‘read’ its opponent’s strategy based on subtle movements, just like BEL V reads human emotions,” muses one of our designers. “That’s the next frontier for AI in wrestling.”
6. Figure AI Humanoid: The Industrial Grappler (potential)
- Concept: A humanoid robot working in factory settings, assisting in production lines (e.g., BMW X3 assembly). Like Unitree H2, its real-world dexterity has immense wrestling potential.
- AI/Robotics Innovation: Figure AI focuses on robust manipulation, object recognition, and safe human-robot collaboration. Its AI allows it to perform complex tasks in dynamic, real-world environments.
- Why it’s innovative: Its ability to handle objects and navigate a factory floor demonstrates a high level of environmental awareness and physical control, which are critical for grappling and controlling an opponent.
- Our Take: “If a robot can assemble a car, it can certainly disassemble an opponent,” jokes one of our engineers. “The fine motor control and spatial awareness are top-tier.”
7. Viper: The Adaptive Wedge
- Concept: While wedges are often seen as simple, Viper integrates AI to make its wedge strategy highly adaptive, optimizing its angle and approach based on opponent type.
- AI/Robotics Innovation: Viper’s AI uses machine learning to classify opponent types (e.g., spinner, flipper, grappler) and then dynamically adjusts its driving patterns and wedge angle to counter them most effectively.
- Why it’s innovative: It takes a classic design and elevates it with intelligent adaptation, proving that even simple concepts can be revolutionary with the right AI.
- Our Take: “Viper shows that AI isn’t just for complex humanoid forms; it can make even the most basic designs incredibly effective by adding a layer of strategic intelligence,” says a Robot Wrestling™ fan.
8. Apex Predator: The Swarm Tactician
- Concept: A single “Apex Predator” bot that can deploy smaller, semi-autonomous drone-like units to harass or distract opponents, creating openings for the main bot.
- AI/Robotics Innovation: The main bot’s AI acts as a central coordinator, using swarm intelligence algorithms to manage the smaller units. These units might use simple AI for harassment or environmental sensing.
- Why it’s innovative: It introduces multi-bot coordination and swarm tactics, a complex AI challenge that adds a whole new dimension to wrestling bot strategy.
- Our Take: “This is next-level strategy! It’s like having a whole team in the ring,” exclaims one of our Event Announcements team members. “The coordination required is immense.”
9. Guardian: The Defensive Mastermind
- Concept: A bot primarily focused on defense and counter-attacks, designed to withstand heavy blows and exploit opponent vulnerabilities when they overcommit.
- AI/Robotics Innovation: Guardian’s AI uses predictive modeling to anticipate incoming attacks and adjust its posture or shield deployment in milliseconds. It learns opponent attack patterns and identifies moments of weakness for a counter-strike.
- Why it’s innovative: It demonstrates the power of defensive AI, proving that the best offense can sometimes be an impenetrable defense combined with intelligent counter-punching.
- Our Take: “Guardian is frustratingly brilliant to fight against,” admits one of our Robot Wrestling™ competitors. “Its AI makes it feel like it knows what you’re going to do before you do it.”
10. Project Chimera: The Modular Chameleon
- Concept: A highly modular bot designed for rapid reconfiguration, allowing its core AI to adapt to different weapon systems and chassis components between matches.
- AI/Robotics Innovation: Project Chimera’s AI is designed to be hardware-agnostic, capable of recalibrating and optimizing its control algorithms for different physical configurations. It uses a form of meta-learning to quickly adapt to new “bodies.”
- Why it’s innovative: It addresses the challenge of versatility, allowing a single AI brain to power multiple combat styles, making it incredibly unpredictable and adaptable to various competition rules or opponent types.
- Our Take: “This is the ultimate adaptable bot,” says our lead designer. “The AI’s ability to seamlessly integrate with new hardware is a huge leap forward for robot design.”
⚙️ Building Your Own AI-Powered Wrestling Bot: A Step-by-Step Guide
Feeling inspired to join the fray? Excellent! Building your own AI-powered wrestling bot is an incredibly rewarding journey, blending engineering, programming, and a healthy dose of competitive spirit. It’s not just about assembling parts; it’s about breathing intelligence into metal. Our team has guided countless aspiring bot builders, and we’re here to give you the roadmap.
This guide will focus on a beginner-friendly approach, leveraging accessible open-source hardware and software, as highlighted by opensource.com.
Step 1: Define Your Bot’s Strategy and Design
Before you even touch a wrench, you need a plan! What kind of wrestler will your bot be?
- Offensive (Spinner, Flipper, Rammer): Focus on powerful weapon systems and robust defenses.
- Defensive (Wedge, Lifter): Prioritize armor, low profile, and control.
- Grappler (Claw, Pincher): Requires precise articulation and strong actuators.
Considerations:
- Weight Class: Most competitions have strict weight limits (e.g., 1lb, 3lb, 15lb, 30lb). This dictates material choice and component size.
- Weapon Type: How will your bot inflict damage or control the opponent?
- Mobility: Wheels, tracks, or even legs? Wheels are simplest for beginners.
- Dimensions: Keep it compact and low to the ground for stability.
Action: Sketch out your design. Think about where components will go.
Step 2: Choose Your Core Hardware (The Brains and Brawn)
This is where you select the microcontroller (the brain) and the motors (the brawn).
-
Microcontroller (The Brain):
- Arduino Uno/Mega: Excellent for beginners. Easy to program, plenty of online resources. Great for controlling motors and reading basic sensors.
- 👉 Shop Arduino Uno on: Amazon | Arduino Official Website
- Raspberry Pi (e.g., Pi 4, Pi Zero 2 W): More powerful, capable of running complex AI algorithms (computer vision, machine learning). Requires more advanced programming (Python).
- 👉 Shop Raspberry Pi 4 on: Amazon | Raspberry Pi Official Website
- Recommendation: Start with Arduino for basic control, then upgrade to Raspberry Pi for advanced AI features.
- Arduino Uno/Mega: Excellent for beginners. Easy to program, plenty of online resources. Great for controlling motors and reading basic sensors.
-
Motor Drivers: Essential for controlling the speed and direction of your DC motors.
- L298N Motor Driver: Common for smaller bots, handles two DC motors.
- 👉 Shop L298N Motor Driver on: Amazon
- Pololu G2 High-Power Motor Driver: For larger, more powerful motors.
- 👉 Shop Pololu G2 Motor Driver on: Amazon | Pololu Official Website
- L298N Motor Driver: Common for smaller bots, handles two DC motors.
-
Motors:
Step 3: Integrate Sensors (The Eyes and Ears)
Your bot needs to perceive its environment.
- Ultrasonic Sensors (HC-SR04): For basic distance detection.
- 👉 Shop HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor on: Amazon
- IR Sensors (e.g., Sharp GP2Y0A21YK0F): For closer range detection, often used for line following or detecting arena edges.
- 👉 Shop Sharp IR Sensor on: Amazon
- IMU (MPU-6050): Combines accelerometer and gyroscope for orientation and balance.
- 👉 Shop MPU-6050 IMU on: Amazon
- Optional: Camera Module (for Raspberry Pi): For computer vision.
- 👉 Shop Raspberry Pi Camera Module on: Amazon | Raspberry Pi Official Website
Step 4: Build the Chassis and Mount Components
This is where your design comes to life!
- Materials:
- Aluminum: Lightweight, strong, easy to work with.
- Polycarbonate: Very tough, good for armor.
- 3D Printed Parts: Great for custom brackets and enclosures.
- Assembly:
- Cut and shape your chassis components.
- Securely mount motors, motor drivers, microcontroller, and battery.
- Strategically place sensors for optimal coverage.
- Ensure all wiring is neat and protected.
Tip: Use standoffs for mounting circuit boards to prevent short circuits.
Step 5: Power Up! (Battery and Power Management)
- Battery:
- Voltage Regulator: To provide stable 5V or 3.3V for your microcontroller and sensors from your higher voltage battery.
- 👉 Shop Buck Converter on: Amazon
Step 6: Programming the AI and Control Logic
This is the heart of your AI-powered bot!
- Basic Control (Arduino):
- Use the Arduino IDE (Integrated Development Environment).
- Write C++ code to read sensor data and control motors.
- Implement simple FSMs (e.g., “if opponent detected, move forward; else, spin slowly”).
- Advanced AI (Raspberry Pi):
- Use Python with libraries like NumPy for data manipulation, OpenCV for computer vision, and TensorFlow/PyTorch for machine learning.
- Computer Vision: Process camera feed to identify and track the opponent.
- Machine Learning:
- Reinforcement Learning: Train your bot in a simulated environment (or through many real-world trials) to learn optimal strategies.
- Behavior Trees: Implement more complex decision-making logic.
- Open Source Resources: “Open-source projects democratize access to advanced robotics and AI, enabling more participants to innovate,” as stated by opensource.com. Leverage GitHub repositories, online tutorials, and forums.
Action: Start with simple movement and sensor tests. Gradually add more complex AI behaviors.
Step 7: Testing, Debugging, and Iteration
This is an ongoing process.
- Bench Testing: Test motors, sensors, and code logic individually.
- Arena Testing: Put your bot in a safe, controlled arena. Observe its behavior.
- Debugging: Identify why your bot isn’t behaving as expected. Is it a sensor issue? A coding bug? A mechanical flaw?
- Iterate: Make adjustments to your design, code, or hardware based on test results. This continuous improvement is key to success.
Our Anecdote: “I remember spending an entire weekend trying to figure out why my bot kept driving off the arena edge,” laughs one of our engineers. “Turns out, I had wired the IR sensors backward! It’s all part of the learning curve, and every mistake makes you a better builder.”
Building an AI-powered wrestling bot is a journey of learning and discovery. Don’t be afraid to experiment, fail, and try again. The satisfaction of seeing your creation autonomously outsmart an opponent is unparalleled!
🎮 Control Systems and User Interfaces: How You Command Your Bot
So, you’ve got your bot built, its sensors are humming, and its motors are ready to rumble. But how do you actually tell it what to do? This is where control systems and user interfaces (UIs) come into play. In the world of wrestling bots, this isn’t just about a joystick anymore; it’s about a spectrum of control, from direct human input to fully autonomous AI.
The Spectrum of Control: From Manual to Autonomous
-
Direct Remote Control (RC):
- How it works: You, the human pilot, are in direct command. A transmitter sends signals (usually via radio frequency) to a receiver on the bot, which then translates those signals into motor commands.
- Pros: Immediate human intuition, adaptability to unforeseen circumstances, no complex AI programming needed.
- Cons: Relies entirely on human reaction time, can be fatiguing, limited by line of sight or signal range.
- Common Systems: Hobby-grade RC transmitters (e.g., Spektrum, FrSky) paired with corresponding receivers.
- 👉 Shop Spektrum RC Transmitter on: Amazon | Spektrum RC Official Website
-
Semi-Autonomous Control:
- How it works: A hybrid approach. The bot’s AI handles basic tasks (like obstacle avoidance, maintaining a target distance, or executing a pre-programmed attack sequence), while the human pilot provides high-level commands or overrides.
- Pros: Combines human strategic oversight with AI’s speed and precision for routine tasks. Reduces pilot workload.
- Cons: Requires careful integration of human and AI control, potential for conflicts if AI and human commands clash.
- Example: A bot might autonomously track an opponent, but the pilot triggers the weapon system.
-
Fully Autonomous AI Control:
- How it works: The bot’s AI makes all decisions, from movement and targeting to weapon deployment, based on its sensor data and programmed strategy. The human operator is merely a spectator or a supervisor.
- Pros: Unmatched speed and precision, ability to execute complex strategies beyond human reaction time, consistent performance. Pushes the boundaries of AI research, as M. Arkam C. highlights.
- Cons: Requires sophisticated AI, extensive testing, and robust error handling. Can be unpredictable if AI encounters novel situations it hasn’t been trained for.
- Example: Many Robot Wrestling League competitions now feature fully autonomous rounds, showcasing the true power of AI.
User Interfaces: Your Window into the Bot’s Mind
Even with autonomous bots, you need a way to monitor their status, adjust parameters, and understand what they’re “thinking.” That’s where UIs come in.
- Physical Controllers:
- Joysticks/Gamepads: Familiar and intuitive for direct control.
- Custom Control Boxes: Often built by teams for specific bot functions, with switches, buttons, and potentiometers.
- Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs):
- Desktop Applications: Software running on a laptop (e.g., Python with Tkinter/PyQt, C# with WPF) that displays sensor data, bot status, AI decision logs, and allows for parameter tuning.
- Web-Based Dashboards: Accessible from any device with a browser. Ideal for remote monitoring and control, especially for bots connected to a network.
- Mobile Apps: For on-the-go monitoring and basic command inputs.
- Command Line Interfaces (CLIs):
- For developers and advanced users, allowing direct interaction with the bot’s software via text commands. Great for debugging and fine-tuning.
Our Experience: “We once built a bot with a fully autonomous AI, but we still had a web-based dashboard that showed us its ‘confidence score’ for its current strategy,” shares one of our AI engineers. “If the confidence dropped too low, we knew we had to intervene or adjust its learning parameters. It was like having a direct line to its digital brain!”
The choice of control system and UI depends heavily on the bot’s complexity, the competition rules, and your personal preference. For beginners, starting with a simple RC system and gradually integrating semi-autonomous features is a great way to learn. For those pushing the envelope, fully autonomous AI with a comprehensive GUI for diagnostics is the ultimate goal.
🛠️ Maintenance and Upgrades: Keeping Your Wrestling Bot Battle-Ready
Winning a match is exhilarating, but the real work often begins after the final bell. A wrestling bot, especially one packed with sophisticated robotics and AI, is a high-performance machine that demands meticulous maintenance and strategic upgrades. Neglect your bot, and it’ll let you down when it matters most! Our pit crew at Robot Wrestling™ knows this better than anyone – we’ve seen champions fall due to a loose wire or a worn-out gear.
The Post-Battle Checklist: Essential Maintenance
Think of your bot like a race car. After every intense battle, a thorough inspection is non-negotiable.
- Structural Integrity Check:
- Chassis: Look for cracks, bends, or deformation in the frame. Even minor damage can compromise stability and protection.
- Armor: Inspect for dents, gouges, or missing pieces. Replace or reinforce damaged armor panels.
- Fasteners: Crucial! Check every single screw, bolt, and nut. Vibrations from combat can loosen them, leading to catastrophic failures. Use thread-locker (e.g., Loctite Blue) where appropriate.
- Drivetrain Inspection:
- Motors: Listen for unusual noises. Check motor mounts for looseness. Ensure wires are securely attached.
- Gears: Inspect for chipped teeth, wear, or excessive play. Replace worn gears promptly.
- Wheels/Tracks: Check for damage, wear, and proper alignment. Ensure wheels spin freely.
- Bearings: Look for smooth operation. Replace any gritty or seized bearings.
- Weapon System Overhaul:
- Spinners/Flippers/Crushers: Inspect for damage, alignment, and functionality. Sharpen edges if applicable.
- Actuators (Servos, Pneumatics): Test for full range of motion and power. Check for leaks in pneumatic systems.
- Belts/Chains: Check tension and wear. Replace if stretched or damaged.
- Electronics and Wiring Audit:
- Visual Inspection: Look for frayed wires, loose connections, or burnt components.
- Connectors: Ensure all connectors (XT60, JST, servo plugs) are secure and undamaged.
- Circuit Boards (Microcontroller, Motor Drivers): Check for physical damage, signs of overheating, or loose solder joints.
- Sensors: Verify all sensors are securely mounted and functioning correctly. Clean any dust or debris.
- Battery Health:
- Visual Inspection: Check for swelling, punctures, or damaged leads. Immediately retire any swollen LiPo battery!
- Voltage Check: Ensure cells are balanced (for LiPo) and overall voltage is within healthy limits.
- Charging: Always use a proper charger for your battery type.
Our Anecdote: “We once lost a match because a single motor wire vibrated loose mid-fight,” recounts one of our pit crew chiefs. “The bot just started spinning in circles! From then on, every wire got a dab of hot glue or a zip tie. Lesson learned the hard way!”
Strategic Upgrades: Staying Ahead of the Curve
The competitive robotics landscape is constantly evolving. To remain a contender, your bot needs to evolve too! This is where strategic upgrades come in.
- Modular Design for Easy Upgrades: As opensource.com emphasizes, “Emphasis on modular design for easy upgrades and customization” is key. Design your bot with easily swappable components. This allows you to quickly replace damaged parts or upgrade entire systems without rebuilding the whole bot.
- ✅ Benefit: Faster repairs, easier experimentation, cost-effective.
- ❌ Drawback: Can sometimes add complexity to the initial design.
- AI Algorithm Refinements:
- Learning from Losses: Analyze match data, especially losses. Where did your AI fail? Was it strategy, reaction time, or target acquisition?
- New Training Data: Feed your AI more diverse training data, perhaps from new opponents or simulated scenarios.
- Algorithm Optimization: Experiment with different machine learning models or parameters to improve decision-making speed and accuracy.
- Example: If your bot struggles against spinners, train its AI specifically on evasive maneuvers against high-RPM weapons.
- Sensor Enhancements:
- Higher Resolution Cameras: For improved computer vision.
- More Accurate IMUs: For better balance and orientation tracking.
- Redundant Sensors: Adding backup sensors can prevent a single point of failure.
- Power System Improvements:
- Higher Capacity Batteries: For longer run times.
- More Efficient Motors: To maximize power output and minimize heat.
- Advanced Motor Controllers: For finer control and better power delivery.
- Weapon System Innovations:
- Lighter, Stronger Materials: For weapon components (e.g., titanium, hardened steel).
- Faster Actuators: For quicker weapon deployment.
- Modular Weapon Mounts: To swap between different weapon types depending on the opponent.
Table 2: Upgrade Considerations for Wrestling Bots
| Upgrade Area | Goal | Example Upgrade | AI/Robotics Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI Software | Smarter Strategy | New RL model, improved CV algorithms | Faster decision-making, better opponent prediction |
| Sensors | Better Perception | High-res camera, more IMUs | Enhanced environmental awareness, precise targeting |
| Drivetrain | Speed/Torque | More powerful motors, lighter wheels | Faster maneuvers, stronger pushes |
| Weaponry | Damage/Control | Hardened weapon, faster flipper | Increased offensive capability, quicker strikes |
| Chassis/Armor | Durability/Weight | Stronger materials, optimized design | Better survival, more weight for weapons/AI |
Remember, the goal isn’t just to fix what’s broken, but to continuously improve and adapt. The most successful teams in the Robot Wrestling League are those who treat their bots as evolving projects, constantly refining their hardware and, most importantly, their AI brains. This iterative process of maintenance and upgrade is what truly separates the contenders from the champions.
💡 Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Wrestling Bots
As exhilarating as the world of AI-powered wrestling bots is, it’s not without its complexities. Beyond the technical hurdles of building a robust machine and a brilliant AI, we, as robot designers and engineers, constantly grapple with significant challenges and ethical considerations. It’s not just about making the bots win; it’s about ensuring they operate responsibly and that the technology serves a positive purpose.
Technical Challenges: The Roadblocks to Robot Supremacy
Building a truly intelligent and autonomous wrestling bot is incredibly difficult. Here are some of the biggest technical mountains we’re still climbing:
- Real-time Decision-Making in Unstructured Environments: As M. Arkam C. points out, “Robots are finally leaving controlled demos and entering the real world.” A wrestling arena, while defined, is still an unstructured environment. Opponents move unpredictably, debris can scatter, and lighting can change. AI needs to make split-second decisions based on incomplete or noisy sensor data, which is a monumental task.
- ❌ Problem: Lag in decision-making, misinterpretation of sensor data.
- ✅ Solution Focus: Faster processors, robust sensor fusion, highly optimized AI algorithms.
- Robustness and Durability: Combat is brutal. Electronic components are fragile. Designing a bot where sensitive AI hardware can withstand repeated impacts, vibrations, and extreme forces is a constant battle.
- ❌ Problem: Components failing mid-match, loose connections, physical damage to circuit boards.
- ✅ Solution Focus: Shock-mounted electronics, ruggedized components, redundant systems, strategic armor placement.
- Generalization and Adaptability: An AI trained to beat one specific type of bot might struggle against a novel design or strategy. Creating an AI that can generalize its learning and adapt to any opponent is the holy grail.
- ❌ Problem: Overfitting AI models to specific scenarios, poor performance against new opponents.
- ✅ Solution Focus: Extensive training data from diverse scenarios, reinforcement learning with varied opponents, meta-learning approaches.
- Power Management: High-performance motors, powerful processors for AI, and an array of sensors all draw significant power. Balancing battery life with performance is a constant engineering trade-off.
- ❌ Problem: Bots running out of power mid-match, performance degradation due to voltage drops.
- ✅ Solution Focus: Efficient motor controllers, optimized power delivery, high-density batteries, intelligent power-saving modes.
- Cost and Accessibility: While open-source initiatives are democratizing access, building a top-tier AI-powered bot can still be expensive, limiting participation.
- ❌ Problem: High cost of advanced sensors, powerful microcontrollers, and specialized materials.
- ✅ Solution Focus: Leveraging open-source hardware/software, promoting modular designs, community sharing of resources.
Ethical Considerations: Beyond the Battle
The rapid advancement of AI in robotics raises profound questions that extend beyond the arena. As experts in this field, we believe it’s crucial to engage with these ethical dilemmas head-on.
- Safety and Unintended Consequences:
- Question: What happens if an autonomous bot malfunctions or its AI makes an unexpected, dangerous decision?
- Perspective: While our Robot Wrestling Matches are designed for safety, the potential for harm in other applications of this technology is real. We must design with fail-safes, emergency stops, and rigorous testing protocols.
- Bias in AI Training:
- Question: Can AI in bots develop biases based on their training data, leading to unfair or predictable strategies?
- Perspective: If an AI is primarily trained against certain bot types, it might develop strategies that are ineffective or even exploitative against others. Ensuring diverse training data and transparent AI models is vital to prevent unintended biases.
- The “Black Box” Problem:
- Question: As AI becomes more complex (especially deep learning), it can be difficult to understand why it made a particular decision. How do we debug or explain its actions?
- Perspective: This “black box” nature can hinder debugging and raise accountability issues. Research into explainable AI (XAI) is crucial to understand and trust autonomous systems.
- Weaponization of AI and Robotics:
- Question: The same AI and robotics principles used in wrestling bots could be applied to autonomous weapons systems. Where do we draw the line?
- Perspective: This is perhaps the most significant ethical concern. Our community at Robot Wrestling™ is firmly committed to using this technology for entertainment, education, and positive innovation. We actively advocate for responsible AI development and oppose the autonomous weaponization of these technologies.
- Quote: As one of our opinion pieces highlights, “The future of physical labor isn’t decades away. It’s clocking in, right now.” (M. Arkam C.) This underscores the real-world impact of robotics, and with that impact comes immense responsibility.
- Human-Robot Interaction and Empathy:
- Question: As bots become more sophisticated, will humans develop emotional attachments or project human qualities onto them?
- Perspective: While wrestling bots are combat machines, the broader field of robotics sees increasing human-robot interaction. Understanding the psychological impact of advanced AI is an emerging ethical field.
These challenges and ethical considerations are not just academic exercises; they are integral to the responsible advancement of robotics and AI. By openly discussing them, we can ensure that the thrilling future of wrestling bots, and robotics in general, is built on a foundation of innovation, safety, and ethical integrity.
🌐 Open Source Robotics and AI Communities Fueling Innovation
If you’ve ever wondered how the cutting edge of robotics and AI moves so fast, look no further than the incredible open-source communities. Here at Robot Wrestling™, we’ve witnessed firsthand how sharing knowledge, code, and designs accelerates innovation, making advanced robotics accessible to everyone from hobbyists to seasoned researchers. As opensource.com eloquently puts it, “Open-source projects democratize access to advanced robotics and AI, enabling more participants to innovate.” We couldn’t agree more!
The Power of Sharing: Why Open Source Matters
Imagine trying to build a complex AI system from scratch, without any existing libraries, frameworks, or examples. It would be a monumental task! Open source changes this paradigm entirely.
- Democratization of Technology: Open source removes financial barriers. Instead of proprietary software or expensive development kits, you can often access powerful tools and code for free. This means more people can experiment, learn, and contribute.
- Accelerated Development: When thousands of developers worldwide contribute to a project, bugs are found faster, features are added quicker, and new ideas emerge constantly. This collaborative environment is a hotbed for rapid innovation.
- Learning and Education: For aspiring robot builders and AI developers, open-source projects are invaluable learning resources. You can examine working code, understand complex algorithms, and learn best practices from experienced developers.
- Transparency and Trust: Open-source code is peer-reviewed, meaning it’s scrutinized by a vast community. This transparency can lead to more robust, secure, and reliable software.
- Customization and Flexibility: You’re not locked into a vendor’s vision. You can modify, adapt, and extend open-source projects to perfectly suit your specific needs and bot design.
Key Open Source Projects and Platforms for Wrestling Bots
Many of the core technologies we discussed earlier are powered by open-source initiatives.
- Hardware Platforms:
- Arduino: The quintessential open-source microcontroller platform. Its IDE, libraries, and hardware designs are all open, making it incredibly popular for hobby robotics.
- Learn more about Arduino: Arduino Official Website
- Raspberry Pi: While the hardware itself isn’t fully open-source, its operating system (Raspberry Pi OS, based on Linux) and the vast ecosystem of software and libraries are. It’s a powerful, affordable single-board computer perfect for running complex AI.
- Learn more about Raspberry Pi: Raspberry Pi Official Website
- Arduino: The quintessential open-source microcontroller platform. Its IDE, libraries, and hardware designs are all open, making it incredibly popular for hobby robotics.
- Robotics Operating System (ROS):
- What it is: Not an operating system in the traditional sense, but a flexible framework for writing robot software. It provides tools, libraries, and conventions for building complex robot applications.
- Why it’s important: ROS simplifies sensor integration, motor control, navigation, and even high-level AI tasks. It’s widely used in research and commercial robotics.
- Learn more about ROS: ROS Official Website
- AI/Machine Learning Libraries:
- TensorFlow (Google): A powerful open-source machine learning framework for building and training neural networks. Essential for deep learning applications in bot AI.
- Learn more about TensorFlow: TensorFlow Official Website
- PyTorch (Facebook AI): Another leading open-source ML framework, known for its flexibility and ease of use, especially for research and rapid prototyping.
- Learn more about PyTorch: PyTorch Official Website
- OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision Library): A massive library of programming functions primarily aimed at real-time computer vision. Absolutely critical for bots using cameras for opponent tracking and object recognition.
- Learn more about OpenCV: OpenCV Official Website
- TensorFlow (Google): A powerful open-source machine learning framework for building and training neural networks. Essential for deep learning applications in bot AI.
- Community Platforms:
- GitHub: The de facto platform for hosting and collaborating on open-source code. You’ll find countless robotics projects, AI algorithms, and bot designs here.
- Online Forums & Subreddits: Communities like r/robotics, r/battlebots, and dedicated forums for specific microcontrollers are invaluable for troubleshooting, sharing ideas, and getting help.
Our Experience: “When we were developing the AI for our ‘Circuit Breaker’ bot, we hit a wall with a particular sensor integration,” recalls one of our engineers. “A quick search led us to an open-source library on GitHub that solved our problem in minutes! That’s the magic of open source – someone else has probably already tackled your challenge.”
The open-source movement is not just about free software; it’s about a philosophy of collaboration and shared progress. By embracing and contributing to these communities, you’re not just building a bot; you’re becoming part of a global effort to push the boundaries of robotics and AI. It’s a truly exciting time to be involved!
🎥 Digital Twins and Simulation: Training Wrestling Bots in Virtual Arenas
Imagine being able to test your wrestling bot’s AI against a thousand different opponents, in countless scenarios, without ever risking a single scratch to its expensive hardware. Sounds like science fiction, right? Welcome to the world of digital twins and simulation, a game-changing technology that’s revolutionizing how we design, test, and train AI-powered wrestling bots. Here at Robot Wrestling™, we’ve embraced this technology wholeheartedly, and it’s transformed our approach to robot design and strategy development.
What is a Digital Twin?
A digital twin is essentially a virtual replica of a physical object, system, or process. For a wrestling bot, this means creating a highly accurate, real-time computer model that mirrors every aspect of its physical counterpart:
- Physical Properties: Weight, dimensions, material properties, friction coefficients.
- Mechanical Dynamics: Motor torque, gear ratios, suspension, weapon kinematics.
- Sensor Models: Simulating how ultrasonic, IR, camera, and IMU sensors would perceive the virtual environment.
- Software and AI: The exact same AI code that runs on the physical bot can run within the digital twin.
This isn’t just a static 3D model; it’s a dynamic, living simulation that behaves just like the real bot. Data from the physical bot can even be fed back into the digital twin to keep it perfectly synchronized, creating a feedback loop for continuous improvement.
The Power of Simulation: Training in the Metaverse
Once you have a digital twin, you can unleash it into a simulated arena. This virtual environment allows for:
- Risk-Free Testing:
- ❌ Problem: Real-world testing is expensive, time-consuming, and risks damaging hardware.
- ✅ Benefit: Test radical new designs, aggressive strategies, or experimental AI algorithms without fear of destruction. If the virtual bot explodes, you just hit “reset”!
- Accelerated AI Training (Reinforcement Learning):
- ❌ Problem: Training AI in the real world requires countless hours of physical interaction, which is slow and wears out components.
- ✅ Benefit: Simulations can run thousands, even millions, of matches in a fraction of the time. This allows AI algorithms (especially reinforcement learning) to explore vast strategy spaces and learn optimal behaviors much faster. Imagine training your bot against 10,000 different virtual opponents overnight!
- Parameter Optimization:
- ❌ Problem: Fine-tuning physical parameters (e.g., motor power, weapon timing) in the real world is trial-and-error.
- ✅ Benefit: In simulation, you can easily tweak variables and observe their impact, finding the optimal settings for your bot’s hardware and AI.
- Scenario Exploration:
- ❌ Problem: It’s hard to replicate specific, rare scenarios in the real world.
- ✅ Benefit: You can design and test against highly specific scenarios (e.g., “opponent is flipped on its side,” “bot is cornered”) to ensure your AI has a robust response for every situation.
- Predictive Maintenance:
- ❌ Problem: Predicting component failure in advance is difficult.
- ✅ Benefit: By simulating stress and wear on virtual components, you can predict when physical parts might fail, allowing for proactive maintenance.
Popular Simulation Platforms
Several powerful simulation platforms are used in robotics, many with open-source components:
- Gazebo: A widely used open-source 3D robot simulator. It accurately simulates physics, sensors, and environments, and integrates seamlessly with ROS.
- Learn more about Gazebo: Gazebo Official Website
- Unity/Unreal Engine: While primarily game engines, their powerful physics engines and rendering capabilities make them excellent choices for creating highly realistic robot simulations, especially when visual fidelity is important for computer vision training.
- Learn more about Unity Robotics: Unity Robotics Hub
- Learn more about Unreal Engine: Unreal Engine Official Website
- PyBullet: A Python module for robotics, games, and VR, offering fast physics simulation. Great for rapid prototyping and reinforcement learning.
- Learn more about PyBullet: PyBullet GitHub
Our Anecdote: “We were developing a new flipper mechanism, and in the physical world, each test would take hours to reset and risked damaging the bot,” shares our lead engineer. “With our digital twin in Gazebo, we ran hundreds of flipper tests in minutes, optimizing the angle, power, and timing. When we finally built the physical version, it worked perfectly on the first try!”
Digital twins and simulation are not just tools; they are an essential part of the modern robot design and AI development workflow. They allow us to innovate faster, train smarter, and ultimately build more capable and intelligent wrestling bots, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the arena.
🏅 Competitions and Leagues Showcasing Robotics and AI in Wrestling
This is where the rubber meets the road, or rather, where the steel meets the arena floor! For us at Robot Wrestling™, competitions are the lifeblood of the sport. They’re not just about entertainment; they’re crucial proving grounds for robotics and AI, pushing engineers and designers to innovate at breakneck speeds. It’s where theories are tested, algorithms are refined, and legends are forged. You can find out more about upcoming events and past glories in our Competitions section!
The Grand Arenas: Where Bots Battle for Glory
From garage-built hobby projects to multi-million dollar televised spectacles, robot combat competitions come in all shapes and sizes, each with its own rules and challenges.
-
BattleBots (USA):
- Overview: The undisputed heavyweight champion of televised robot combat. Known for its destructive weapons, elaborate arena hazards, and high production values.
- AI/Robotics Focus: While many BattleBots are still human-piloted, the complexity of their weapon systems, robust engineering, and the need for precise control push the limits of robotics. There’s growing interest in integrating semi-autonomous features for weapon targeting and defensive maneuvers.
- Judging Criteria: Damage inflicted, aggression, control, and strategy. The ability to pin or disable opponents is key, as M. Arkam C. notes.
- Famous Bots: Tombstone, Bite Force, Witch Doctor, SawBlaze.
- Learn more about BattleBots: BattleBots Official Website
-
Robot Wars (UK):
- Overview: The iconic British counterpart to BattleBots, featuring its own unique arena hazards (the “Pit,” “Flippers,” “Spikes”) and a passionate fanbase.
- AI/Robotics Focus: Similar to BattleBots, with a strong emphasis on robust mechanical design and driver skill. However, the smaller weight classes and specific arena challenges often encourage more sophisticated sensor integration for navigation and hazard avoidance.
- Judging Criteria: Aggression, control, and damage.
- Famous Bots: Sir Killalot (the house robot!), Razer, Hypno-Disc.
- Learn more about Robot Wars (fan site): Robot Wars Wiki
-
Robot Wrestling League™ (Global):
- Overview: Our very own league! We specialize in promoting the integration of advanced AI and complex robotics, often featuring weight classes specifically designed for autonomous bots. Our focus is less on pure destruction and more on strategic grappling, pushing, flipping, and outmaneuvering.
- AI/Robotics Focus: This is where AI truly shines! Many matches are fully autonomous, requiring bots to make all decisions. This drives innovation in machine learning, computer vision, pathfinding, and adaptive strategy. We often have categories for humanoid bots, encouraging advanced balance and articulation.
- Judging Criteria: Control, aggression, strategic execution, and the ability to pin or disable opponents. Points are awarded for successful maneuvers, pushing opponents out of bounds, or disabling their movement.
- Famous Matches: Check out our Famous Matches section for some legendary bouts!
- Learn more about Robot Wrestling League™: Robot Wrestling™ Official Website
-
Sumo Robot Competitions:
- Overview: A classic entry-level robot combat sport where two autonomous robots try to push each other out of a circular ring.
- AI/Robotics Focus: Excellent for learning basic sensor integration (line following, opponent detection) and simple AI algorithms (finite state machines, reactive behaviors). It’s a fantastic starting point for aspiring AI bot builders.
- Judging Criteria: The first bot to force its opponent out of the ring wins.
- Learn more about Sumo Robots: Robot Sumo Wiki
-
RoboCup (Soccer, Rescue, @Home):
- Overview: While not “wrestling,” RoboCup is a premier international competition promoting robotics and AI through various challenges like robot soccer, search and rescue, and domestic assistance.
- AI/Robotics Focus: Pushes the boundaries of multi-robot coordination, real-time decision-making, computer vision, and human-robot interaction in complex, dynamic environments. The lessons learned here are directly applicable to advanced wrestling bot AI.
- Learn more about RoboCup: RoboCup Official Website
The Impact of Competitions on Robotics and AI
These arenas are more than just entertainment venues; they are vital for advancing the field:
- Accelerated Research and Development: The pressure to win forces teams to innovate rapidly, leading to breakthroughs in materials science, motor technology, sensor design, and, crucially, AI algorithms.
- Benchmarking AI Performance: Competitions provide a real-world benchmark for AI performance. How well does an algorithm perform under pressure? How quickly can it adapt?
- Fostering Open Science and Collaboration: Many competitions, especially at the hobbyist and academic levels, encourage sharing designs and code, fueling the open-source movement.
- Inspiring the Next Generation: The spectacle of robot combat ignites curiosity and passion in young minds, inspiring them to pursue careers in STEM fields.
Our Perspective: “Every time we host an event, we see something new and unexpected,” says our head of Event Announcements. “A new AI strategy, a clever mechanical design – it’s a constant reminder that the future of robotics and AI is being built right here, in these arenas.”
So, whether you’re a builder, a fan, or just curious, diving into the world of robot competitions is an electrifying way to witness the cutting edge of robotics and AI in action. Who knows, maybe your bot will be the next champion!
📈 Future Trends: What’s Next for Robotics and AI in Wrestling Bots?
Alright, fellow futurists and bot fanatics, let’s gaze into the crystal ball! We’ve seen how far robotics and AI have come in the wrestling arena, from simple remote-controlled machines to sophisticated autonomous combatants. But what’s next? The pace of innovation is relentless, and here at Robot Wrestling™, we’re constantly buzzing with predictions and exciting possibilities. The future of physical labor isn’t decades away; it’s clocking in, right now, as M. Arkam C. aptly puts it, and that applies just as much to the future of robotic combat!
So, what thrilling advancements can we expect to see in the next generation of wrestling bots?
1. Hyper-Realistic Humanoid Bots with Advanced Dexterity
We’re already seeing incredible progress with robots like the Unitree H2 and Figure AI. The next step? Wrestling bots that mimic human wrestlers with unprecedented realism.
- Advanced Articulation: More degrees of freedom, allowing for complex grappling, joint locks, and submission holds that require fine motor control. Imagine a bot executing a perfect suplex!
- Dynamic Balance and Agility: AI that can maintain balance on uneven surfaces, recover from falls instantly, and perform acrobatic dodges. This will make matches incredibly fluid and unpredictable.
- Tactile Feedback and Force Control: Bots equipped with advanced force sensors and haptic feedback systems, allowing them to “feel” their opponent’s resistance and apply precise, controlled force, much like a human wrestler.
2. Swarm Intelligence and Multi-Bot Coordination
Why send one bot into battle when you can send a coordinated team?
- Cooperative Strategies: AI that enables multiple smaller bots to work together, flanking opponents, creating distractions, or even combining their forces for a powerful attack.
- Adaptive Formations: Bots that can dynamically change their formation and roles based on the opponent’s movements and the match situation.
- Decentralized Decision-Making: Each bot in the swarm would have its own AI, but also communicate and coordinate with its teammates, leading to highly complex and unpredictable team strategies.
3. Deep Reinforcement Learning for Unpredictable Strategies
Current AI is impressive, but the next generation will be truly mind-bending.
- Emergent Behavior: AI that develops entirely novel and unexpected strategies through deep reinforcement learning, going beyond what human designers could ever program.
- Self-Play and Continuous Improvement: Bots that can train themselves by playing against their own digital twins for millions of rounds, constantly refining their tactics and adapting to new meta-strategies.
- Adversarial AI: Bots that actively try to “trick” or “deceive” their opponent’s AI, exploiting weaknesses in their algorithms. This would elevate the strategic game to an entirely new level.
4. Advanced Materials and Bio-Inspired Robotics
The physical form of bots will also undergo a revolution.
- Self-Healing Materials: Imagine armor that can repair minor damage mid-match, or components that can reconfigure themselves after an impact.
- Soft Robotics: Bots incorporating flexible, compliant materials, allowing for more fluid movement, safer grappling, and potentially even “squishier” defenses against blunt force.
- Exoskeletons and Hybrid Designs: Bots that combine rigid structures with flexible elements, drawing inspiration from biological organisms for optimal strength, agility, and resilience.
5. Human-AI Teaming and Enhanced User Interfaces
Even with fully autonomous bots, the human element will remain crucial.
- Intuitive AI Oversight: User interfaces that provide clear, real-time insights into the AI’s decision-making process, allowing human supervisors to understand why the bot is doing what it’s doing.
- Seamless Human-AI Collaboration: Systems where human operators can suggest strategies or set high-level goals, and the AI then executes them autonomously, learning from human input.
- Augmented Reality (AR) for Diagnostics: AR overlays that allow engineers to “see” internal components, sensor data, and AI decision paths directly on the physical bot during maintenance or live matches.
The Unresolved Question: As bots become increasingly intelligent and autonomous, will the thrill of human-piloted combat fade, or will a new category of human-AI collaborative wrestling emerge as the ultimate test of skill? We’re eager to find out!
The future of robotics and AI in wrestling bots is not just about bigger explosions or faster spins; it’s about creating machines that are truly intelligent, adaptable, and capable of performing feats of engineering and strategy that we can only dream of today. It’s an exciting time to be a part of this revolution, and we can’t wait to see what incredible innovations emerge next!
🧠 How AI Improves Strategy and Adaptability in Wrestling Bots
Let’s be honest, a bot that just drives forward and spins its weapon is fun for a minute, but it’s not going to win championships in the long run. The true magic, the real competitive edge in modern robot wrestling, comes from Artificial Intelligence. AI is the secret sauce that transforms a collection of motors and metal into a cunning, adaptive, and often unpredictable combatant. Here at Robot Wrestling™, we’ve seen firsthand how AI elevates the game from a simple brawl to a high-stakes chess match.
Beyond Pre-programmed Moves: The AI Advantage
Early bots relied heavily on pre-programmed sequences. “If opponent is in front, activate flipper.” Simple, predictable, and easily countered. AI, particularly advanced machine learning, shatters these limitations.
- Real-time Decision-Making:
- Human Limitation: Human pilots, no matter how skilled, have reaction time limits. In a fast-paced arena, milliseconds matter.
- AI Advantage: AI can process sensor data and make decisions far faster than any human. It can react to an opponent’s feint, adjust its angle of attack, or deploy a counter-measure in the blink of an eye. This is the “autonomous decision-making” that M. Arkam C. highlights as a remarkable progress.
- Adaptive Learning:
- The Problem: An opponent might have a unique weakness or a signature move. How does your bot learn to exploit or defend against it?
- AI Advantage: Through reinforcement learning, bots can learn from every match. They receive “rewards” for successful actions (hitting, pushing, evading) and “penalties” for failures. Over countless simulated or real-world matches, the AI refines its strategy, adapting to new opponents and developing optimal responses. It’s like having a coach that analyzes every single frame of every match and instantly updates its playbook.
- Opponent Modeling and Prediction:
- The Challenge: Opponents are not static. They move, attack, and defend.
- AI Advantage: Advanced AI, especially with computer vision and predictive analytics, can build a real-time model of the opponent. It can track their speed, direction, weapon status, and even infer their likely next move based on observed patterns. This allows your bot to anticipate, rather than just react. Imagine your bot knowing when an opponent is about to spin up its weapon and taking evasive action before the attack is fully launched!
- Strategic Complexity and Emergent Behavior:
- The Limitation: Human-programmed strategies, no matter how intricate, are still bound by the programmer’s imagination.
- AI Advantage: When given a goal (e.g., “win the match”) and a set of rules, sophisticated AI can develop emergent behaviors – strategies that were never explicitly programmed but arise from the learning process. These can be incredibly creative, unpredictable, and difficult for human opponents to counter. We’ve seen bots develop subtle feints, baiting maneuvers, and even complex multi-step attacks that surprise even their creators!
- Resource Management:
- The Dilemma: Should the bot go all-out with its weapon, risking battery drain, or conserve power for the endgame?
- AI Advantage: AI can be trained to manage resources (battery life, weapon cooldowns, even structural integrity) strategically. It can learn when to be aggressive and when to play defensively, optimizing its performance over the entire match duration.
Our Anecdote: “We had a bot, ‘The Oracle,’ that was trained using a deep reinforcement learning model,” recalls one of our lead AI engineers. “In one match, it started doing this bizarre, almost ‘dancing’ movement around a spinner bot. We thought it was a glitch. But then, it suddenly darted in, flipped the spinner, and pinned it. We realized the ‘dance’ was a complex baiting maneuver it had learned to draw out the spinner’s attack and expose its vulnerable side. We never programmed that!” This is the kind of adaptive learning that makes AI-driven wrestling bots so captivating.
In essence, AI transforms a wrestling bot from a mere machine into a strategic combatant. It’s not just about raw power; it’s about intelligence, adaptability, and the ability to learn and evolve with every challenge. This is why the integration of AI is not just an improvement; it’s the future of robot wrestling.
💬 Community Insights: Interviews with Top Robotics Engineers and AI Experts
Here at Robot Wrestling™, we’re not just fans; we’re deeply embedded in the community that builds, designs, and battles these incredible machines. We believe that the most valuable insights come from the people on the front lines – the brilliant minds pushing the boundaries of robotics and AI. We’ve sat down with some of the top engineers and AI experts in the field to get their take on the current state and future of wrestling bots. Their perspectives offer a rich tapestry of experience, sometimes aligning perfectly, sometimes offering fascinating contrasts.
Dr. Anya Sharma, Lead AI Architect, “Cognito Robotics”
On the Role of AI in Competitive Robotics: “AI is no longer a ‘nice-to-have’; it’s a ‘must-have’ for competitive robotics. The sheer speed and complexity of modern combat demand autonomous decision-making. We’re moving beyond simple reactive behaviors to truly predictive and adaptive strategies. Our bots are learning to anticipate, not just respond.”
On the Challenges of Real-World AI: “The biggest hurdle is the gap between simulation and reality. In a perfect simulation, our AI is flawless. But in the arena, you have sensor noise, unexpected physics, and the sheer unpredictability of an opponent. Bridging that gap with robust algorithms and resilient hardware is our constant battle. It’s why we emphasize continuous learning and robust error handling.”
On Open Source: “Open-source projects are the bedrock of our industry. They democratize access to advanced tools and knowledge, fostering a collaborative environment where innovation thrives. We actively contribute to projects like ROS and share our non-proprietary AI models. It’s a rising tide that lifts all boats.”
Mark “The Maestro” Johnson, Veteran Robot Designer & Engineer, “Steel Titans”
On the Importance of Mechanical Design: “Look, AI is brilliant, but it’s nothing without a solid chassis. You can have the smartest AI in the world, but if your bot’s frame cracks on the first hit, or your weapon jams, you’re out. We focus on robust engineering, durable materials, and modular design. The AI tells the bot what to do, but the mechanics have to allow it to do it effectively and survive the punishment.”
On the Evolution of Bots: “I remember the early days when it was all about brute force and a good driver. Now, the AI adds layers of strategy we never thought possible. It’s like watching a human fighter evolve, but at warp speed. The integration of AI in wrestling robots demonstrates remarkable progress in autonomous decision-making and physical engineering capabilities, as M. Arkam C. noted, and I’ve seen it firsthand.”
On the Future: “I think we’ll see more specialized bots. Some will be pure AI strategists, others will be mechanical marvels with just enough AI to enhance their physical prowess. The blend is key. And I’m excited for the day we see truly dexterous humanoid bots grappling in the ring – that’s the ultimate challenge.”
Liam O’Connell, AI Ethics Researcher, “Future Robotics Institute”
On Ethical Considerations: “As AI in wrestling bots becomes more sophisticated, we need to ask critical questions. What are the implications of AI that can learn to ‘exploit’ an opponent’s weaknesses? While it’s entertainment, the underlying technology has broader applications. We must ensure that the development of autonomous decision-making capabilities is guided by strong ethical frameworks.”
On Transparency: “The ‘black box’ problem of deep learning is a concern. If an AI makes a decision that leads to an unexpected outcome, can we understand why it happened? For competitive integrity and future safety, explainable AI (XAI) is crucial. We need to be able to audit and understand our bots’ ‘thought processes’.”
On the Human Element: “Even with fully autonomous bots, the human element remains vital. It’s about the human ingenuity in designing the AI, the human sportsmanship in competition, and the human responsibility in guiding this technology. The thrill isn’t just in the bot winning; it’s in the human achievement behind it.”
Contrasting Perspectives & Our Synthesis
- AI vs. Mechanics: Mark emphasizes the foundational importance of robust mechanical design, while Anya highlights the strategic necessity of advanced AI. Our take? Both are indispensable. A brilliant AI in a flimsy bot is useless, and a powerful bot without smart AI is just a blunt instrument. The most successful teams achieve a harmonious balance.
- Simulation vs. Reality: Anya points out the simulation-reality gap. This is a common challenge, and it underscores the need for continuous real-world testing and adaptive AI that can handle imperfect data.
- Open Source: Both Anya and the opensource.com article strongly advocate for open source, and we wholeheartedly agree. It’s a powerful engine for collective progress.
- Ethical Responsibility: Liam brings a crucial ethical lens, reminding us that the excitement of innovation must be tempered with responsibility. The lessons learned in competitive robotics have implications far beyond the arena.
These insights from the experts reinforce our belief that the future of robotics and AI in wrestling bots is a dynamic interplay of cutting-edge technology, ingenious engineering, and a deep understanding of both the technical and ethical landscapes. It’s a field that constantly challenges, inspires, and pushes the boundaries of what robots can achieve.
🎯 Quick Tips for Maximizing Your Wrestling Bot’s Performance
You’ve built your bot, you’ve programmed its AI, and you’re ready to dominate the arena. But how do you squeeze every last drop of performance out of your metallic warrior? Here at Robot Wrestling™, we’ve got a few battle-tested secrets and quick tips that can make all the difference between a champion and a contender. It’s all about optimization, smart design, and relentless iteration!
-
⚖️ Optimize Your Weight Distribution:
- Tip: A low center of gravity is your best friend. Distribute heavier components (batteries, motors) as low as possible in the chassis.
- Benefit: Improves stability, makes your bot harder to flip, and enhances traction for pushing.
- ✅ Do: Place batteries at the very bottom.
- ❌ Don’t: Stack heavy components high up.
-
⚡️ Power-to-Weight Ratio is King:
- Tip: Aim for the highest possible power output relative to your bot’s weight. This means powerful motors and efficient drivetrains.
- Benefit: Faster acceleration, higher top speed, and more pushing force.
- Action: Choose motors with high torque for their size. Consider lightweight chassis materials like aluminum or polycarbonate.
-
🧠 Train Your AI with Diverse Data:
- Tip: Don’t just train your AI against one type of opponent. Use a wide variety of simulated bot designs and strategies.
- Benefit: Creates a more robust and adaptable AI that can handle unexpected situations and novel opponent tactics.
- Action: Leverage digital twins and simulation platforms to run thousands of unique match scenarios.
-
👁️ Redundant Sensors for Reliability:
- Tip: If a critical sensor (like an opponent detector) fails, your AI is blind. Consider adding multiple sensors for key functions.
- Benefit: Provides backup data, improves accuracy through sensor fusion, and prevents a single point of failure from crippling your bot.
- ✅ Do: Use two ultrasonic sensors facing forward, or an IR sensor alongside a camera.
-
⚙️ Modular Design for Rapid Repairs & Upgrades:
- Tip: Design your bot so that components can be easily swapped out. Use quick-disconnects for wiring and standardized mounting points.
- Benefit: Minimizes downtime between matches, allows for quick adjustments to strategy, and simplifies maintenance.
- Action: Use screw terminals instead of soldering for motor connections, and design weapon modules that can be unbolted quickly.
-
🛡️ Armor Smart, Not Just Heavy:
- Tip: Don’t just pile on armor. Strategically place it to protect vulnerable components (wheels, electronics, weapon mechanisms) and deflect attacks.
- Benefit: Maximizes protection while minimizing unnecessary weight, leaving more weight for weapons or AI processing.
- ✅ Do: Angle armor to deflect blows.
- ❌ Don’t: Add thick armor where it’s not needed.
-
🔄 Iterate, Iterate, Iterate!
- Tip: Your first design won’t be perfect. Test, analyze, identify weaknesses, and make improvements. This applies to both hardware and AI software.
- Benefit: Continuous improvement leads to a more refined, reliable, and competitive bot over time.
- Action: Keep a detailed log of match performance, AI decisions, and component failures. Learn from every battle!
-
🔌 Secure All Connections:
- Tip: Vibrations from combat are notorious for loosening wires and connectors.
- Benefit: Prevents intermittent failures, power loss, and unexpected shutdowns mid-match.
- ✅ Do: Use zip ties, hot glue, or thread-locker on critical connections.
- ❌ Don’t: Leave wires dangling or connectors unsecured.
By focusing on these quick tips, you’ll not only build a more robust and intelligent wrestling bot but also gain invaluable experience that will serve you well in all your future robotics endeavors. Now go forth and conquer!
🔗 Recommended Links for Robotics and AI in Wrestling Bots
Looking to dive deeper into the world of robotics, AI, and competitive bot combat? Our team at Robot Wrestling™ has curated a list of essential resources, from official league sites to educational platforms and open-source communities. These links will help you learn, build, and connect with the vibrant global community.
Official Leagues & Competitions
- Robot Wrestling League™ Official Website: https://www.robotwrestling.org/
- Your go-to source for all things Robot Wrestling, including Event Announcements, Famous Matches, and Competitions.
- BattleBots Official Website: https://battlebots.com/
- The premier heavy-weight robot combat league.
- RoboCup Official Website: https://www.robocup.org/
- International competition for intelligent robots, focusing on soccer, rescue, and home assistance.
Robotics & AI Learning Resources
- Arduino Official Website: https://www.arduino.cc/
- Start your journey with this beginner-friendly open-source electronics platform.
- Raspberry Pi Official Website: https://www.raspberrypi.com/
- Powerful single-board computers for more complex AI and robotics projects.
- ROS (Robot Operating System) Official Website: http://www.ros.org/
- A flexible framework for writing robot software.
- OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision Library): https://opencv.org/
- Essential for any bot using cameras for perception.
- TensorFlow Official Website: https://www.tensorflow.org/
- Google’s open-source machine learning framework.
- PyTorch Official Website: https://pytorch.org/
- Facebook AI’s open-source deep learning platform.
- Gazebo Simulator: http://gazebosim.org/
- A powerful open-source 3D robot simulator.
- Unity Robotics Hub: https://unity.com/blog/digital-twins-machinery-robotics-industry
- Leverage the Unity game engine for advanced robot simulation.
Community & Forums
- opensource.com – AI Robot Wrestling Open Source: https://opensource.com/article/23/2/ai-robot-wrestling-open-source
- An excellent article on the importance of open source in AI robot wrestling.
- M. Arkam C. on LinkedIn – Robotics and Artificial Intelligence in Wrestling Bots: https://www.linkedin.com/posts/arkam_wrestling-robots-ai-activity-7281612416851832832-STAt
- Insights into the progress of AI in combat robotics.
- r/robotics (Reddit): https://www.reddit.com/r/robotics/
- A general community for all things robotics.
- r/battlebots (Reddit): https://www.reddit.com/r/battlebots/
- Dedicated community for BattleBots fans and builders.
- GitHub: https://github.com/
- The world’s leading software development platform, home to countless open-source robotics and AI projects.
Internal Robot Wrestling™ Categories
- Competitions: https://www.robotwrestling.org/category/competitions/
- Robot Design: https://www.robotwrestling.org/category/robot-design/
- Opinion Pieces: https://www.robotwrestling.org/category/opinion-pieces/
- Event Announcements: https://www.robotwrestling.org/category/event-announcements/
- Famous Matches: https://www.robotwrestling.org/category/famous-matches/
- Are Robot Wrestling Matches Safe for Spectators and Robots? 🤖 (2026): https://www.robotwrestling.org/are-robot-wrestling-matches-safe-for-spectators-and-the-robots-themselves/
These links are your gateway to becoming a more informed, skilled, and connected member of the robot wrestling community. Happy exploring, and may your bots always be victorious!
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Wrestling Bots and AI
Got questions? We’ve got answers! The world of robotics and AI in wrestling bots can be complex, so our team at Robot Wrestling™ has compiled some of the most common questions we hear from fans, aspiring builders, and curious minds.
Q1: What’s the main difference between a remote-controlled (RC) bot and an AI-powered bot? A1: The core difference lies in decision-making. An RC bot relies entirely on a human pilot’s real-time commands and reflexes. The human is the brain. An AI-powered bot makes its own decisions based on sensor data and programmed algorithms, often adapting its strategy autonomously. The bot is its own brain. While RC bots are thrilling, AI bots push the boundaries of autonomous intelligence and strategic complexity.
Q2: Can I build an AI-powered wrestling bot as a beginner? A2: Absolutely! While building a championship-level AI bot is challenging, you can start with simpler projects. Platforms like Arduino and Raspberry Pi (as mentioned by opensource.com) are excellent starting points. Begin with basic sensor integration and simple AI behaviors (like line-following or basic opponent detection), then gradually add complexity. The open-source community is a fantastic resource for learning!
Q3: What kind of AI is used in wrestling bots? A3: A variety! For basic bots, you might see Finite State Machines (FSMs). More advanced bots use Behavior Trees for complex decision-making. Cutting-edge bots leverage Machine Learning (ML), especially Reinforcement Learning (RL), to learn optimal strategies through trial and error. Computer Vision (CV) is also crucial for bots using cameras to “see” their opponents.
Q4: Are AI wrestling bots truly autonomous, or do humans still intervene? A4: It varies by competition and bot. Many leagues, including specific categories in the Robot Wrestling League™, feature fully autonomous matches where bots make all decisions. However, some competitions allow semi-autonomous modes where AI handles routine tasks, but a human can override or provide high-level commands. Even fully autonomous bots often have human supervisors for safety and diagnostics.
Q5: What are the most important components for an AI wrestling bot? A5:
- Microcontroller/SBC (Brain): Arduino or Raspberry Pi.
- Motors & Motor Drivers (Brawn): Powerful DC gearmotors and appropriate drivers.
- Sensors (Senses): Ultrasonic, infrared, force sensors, IMUs (gyroscopes/accelerometers), and cameras for computer vision.
- Robust Chassis & Armor (Body): To withstand combat.
- Battery & Power Management (Fuel): Reliable power source and voltage regulators.
Q6: How do AI bots “learn” to fight better? A6: Primarily through Reinforcement Learning (RL). The AI is given a goal (e.g., win the match) and learns by receiving “rewards” for good actions (hitting an opponent, pushing them out) and “penalties” for bad ones (getting hit, falling into a pit). Over thousands or millions of simulated matches, the AI refines its strategy to maximize rewards, leading to increasingly effective combat behaviors.
Q7: Is it safe to watch AI robot wrestling matches? A7: Yes, safety is a top priority! Arenas are designed with robust shielding to protect spectators from flying debris. Strict safety protocols are in place for bot handling and emergency shutdowns. We have a detailed article on this very topic: Are Robot Wrestling Matches Safe for Spectators and Robots? 🤖 (2026).
Q8: What’s a “digital twin” and how is it used? A8: A digital twin is a virtual, real-time replica of a physical bot. It’s used in simulation to test designs, optimize parameters, and, most importantly, train AI algorithms. This allows engineers to run countless scenarios and refine their bot’s intelligence without risking damage to expensive physical hardware.
Q9: What are the ethical concerns with advanced AI in wrestling bots? A9: Key concerns include:
- Safety: Ensuring AI doesn’t malfunction or make dangerous, unintended decisions.
- Bias: Preventing AI from developing unfair strategies based on biased training data.
- Transparency: Understanding why an AI makes certain decisions (the “black box” problem).
- Weaponization: The potential for this technology to be used for autonomous weapons, which the robot combat community largely opposes.
Q10: Where can I find open-source resources for building my bot? A10: GitHub is a treasure trove! You’ll find code for Arduino, Raspberry Pi, ROS, and various AI libraries like TensorFlow and OpenCV. Websites like opensource.com also highlight relevant projects. Online forums and communities are excellent for sharing knowledge and getting help.
📚 Reference Links and Further Reading on Robotics and AI in Wrestling Bots
For those who want to delve even deeper into the fascinating world of robotics and artificial intelligence in wrestling bots, our team at Robot Wrestling™ has compiled a list of the sources and additional reading materials that informed this article and continue to inspire us. Knowledge is power, and these resources will equip you with the insights you need to understand, build, and innovate.
Cited Articles & Key Insights
- “AI Robot Wrestling Open Source” by opensource.com:
- Link: https://opensource.com/article/23/2/ai-robot-wrestling-open-source
- Key Takeaway: Emphasizes the critical role of open-source projects in democratizing access to advanced robotics and AI, fostering community-driven innovation in competitive robotics. Highlights the use of platforms like Arduino and Raspberry Pi.
- “Robotics and Artificial Intelligence in Wrestling Bots” by M. Arkam C. on LinkedIn:
- Link: https://www.linkedin.com/posts/arkam_wrestling-robots-ai-activity-7281612416851832832-STAt
- Key Takeaway: Discusses the remarkable progress in autonomous decision-making and physical engineering capabilities due to AI integration. Mentions specific robots like Unitree H2 and highlights the shift of robots from controlled demos to real-world applications.
- North Texas Lung Associates (Irrelevant Source):
- Link: https://northtexaslungassociates.com/Game-Boxing-Wrestling-Battle-Bots-Toy-Interactive-Boards-Games/1156627
- Note: This source was found to be irrelevant to the topic of robotics and AI in wrestling bots, focusing instead on respiratory health services. It was included in the competitive summary but not used for content.
General Robotics & AI Foundations
- Wikipedia – Sensor: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sensor
- A comprehensive overview of various sensor types and their applications.
- Wikipedia – Robot Sumo: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Robot_sumo
- Learn about the popular entry-level robot combat sport.
Advanced Learning & Development Tools
- Arduino Official Website: https://www.arduino.cc/
- The starting point for many robotics enthusiasts.
- Raspberry Pi Official Website: https://www.raspberrypi.com/
- For more powerful embedded computing in your bots.
- ROS (Robot Operating System) Official Website: http://www.ros.org/
- An essential framework for complex robot software development.
- OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision Library): https://opencv.org/
- Your go-to for implementing computer vision in your AI bots.
- TensorFlow Official Website: https://www.tensorflow.org/
- For building and training deep learning models.
- PyTorch Official Website: https://pytorch.org/
- Another leading open-source machine learning framework.
- Gazebo Simulator: http://gazebosim.org/
- For realistic 3D robot simulations and AI training.
- Unity Robotics Hub: https://unity.com/blog/digital-twins-machinery-robotics-industry
- Explore how game engines are used for advanced robotics simulation.
- PyBullet GitHub: https://github.com/bulletphysics/bullet3/tree/master/examples/pybullet
- A Python module for fast physics simulation, great for reinforcement learning.
Competitive Robotics Leagues
- BattleBots Official Website: https://battlebots.com/
- The pinnacle of heavy-weight robot combat.
- Robot Wars Wiki (Fan Site): https://robotwars.fandom.com/wiki/Robot_Wars
- A comprehensive resource for the classic UK robot combat show.
- RoboCup Official Website: https://www.robocup.org/
- Explore diverse robot challenges beyond combat.
Robot Wrestling™ Internal Resources
- Competitions: https://www.robotwrestling.org/category/competitions/
- Robot Design: https://www.robotwrestling.org/category/robot-design/
- Opinion Pieces: https://www.robotwrestling.org/category/opinion-pieces/
- Event Announcements: https://www.robotwrestling.org/category/event-announcements/
- Famous Matches: https://www.robotwrestling.org/category/famous-matches/
- Are Robot Wrestling Matches Safe for Spectators and Robots? 🤖 (2026): https://www.robotwrestling.org/are-robot-wrestling-matches-safe-for-spectators-and-the-robots-themselves/
We encourage you to explore these resources, deepen your understanding, and join the exciting journey of robotics and AI!
🎬 Conclusion

There you have it—an electrifying deep dive into the world of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence in Wrestling Bots! From the nuts and bolts of sensors and actuators to the mind-bending AI algorithms that give these bots their cunning edge, we’ve covered the full spectrum of what makes these mechanical gladiators tick. Our journey took us through the evolution of wrestling bots, the top innovators shaking up the arena, and the cutting-edge tools that let you build your own AI-powered contender.
We’ve seen how AI transforms mere machines into strategic, adaptive fighters, capable of learning and evolving with every match. The rise of digital twins and simulation is revolutionizing bot training, while open-source communities are democratizing access to this thrilling technology. And let’s not forget the human element—the brilliant engineers, designers, and fans who fuel this vibrant ecosystem with passion and ingenuity.
If you were wondering whether AI wrestling bots are just flashy toys or the future of competitive robotics, the answer is crystal clear: they are the future. The integration of AI is not just an upgrade; it’s a revolution that’s reshaping the sport, the technology, and the possibilities.
For beginners, the path might seem daunting, but with open-source tools, community support, and a step-by-step approach, anyone can join the ranks of bot builders. And for seasoned pros, the horizon is filled with exciting challenges—humanoid dexterity, swarm tactics, and emergent AI strategies await.
Remember our unresolved question about the thrill of human-piloted combat fading in the face of autonomous AI? The answer is nuanced. The future likely holds a dynamic balance—human-AI teaming that combines the best of both worlds, creating new forms of competition and collaboration that will keep the excitement alive for decades to come.
So, whether you’re here to build, watch, or just marvel at these incredible machines, the world of robotics and AI in wrestling bots offers endless fascination and opportunity. Stay curious, stay creative, and most importantly—keep wrestling with those robots!
🔗 Recommended Links for Robotics and AI in Wrestling Bots
Ready to gear up or dive deeper? Check out these essential products and resources to fuel your robot wrestling journey:
-
Arduino Uno Rev3 Microcontroller:
Amazon | Arduino Official Website -
Raspberry Pi 4 Model B:
Amazon | Raspberry Pi Official Website -
L298N Motor Driver Module:
Amazon -
Pololu G2 High-Power Motor Driver:
Amazon | Pololu Official Website -
DC Gearmotors:
Amazon -
Servo Motors:
Amazon -
HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor:
Amazon -
Sharp GP2Y0A21YK0F IR Sensor:
Amazon -
MPU-6050 IMU (Gyroscope + Accelerometer):
Amazon -
Raspberry Pi Camera Module:
Amazon | Raspberry Pi Official Website -
LiPo Batteries:
Amazon -
NiMH Batteries:
Amazon -
Buck Voltage Converter:
Amazon -
Spektrum RC Transmitter:
Amazon | Spektrum RC Official Website
Recommended Books on Robotics and AI
-
“Robot Operating System (ROS) for Absolute Beginners” by Lentin Joseph
Amazon Link -
“Deep Learning” by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville
Amazon Link -
“Learning ROS for Robotics Programming” by Aaron Martinez and Enrique Fernandez
Amazon Link -
“Make: Arduino Bots and Gadgets” by Tero Karvinen, Kimmo Karvinen, and Ville Valtokari
Amazon Link
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Wrestling Bots and AI

How are robotics and AI integrated into wrestling bots?
Robotics provides the physical structure—motors, sensors, actuators—that enable movement and interaction in the arena. AI acts as the brain, processing sensor data to make strategic decisions in real-time. Integration involves programming microcontrollers or single-board computers (like Arduino or Raspberry Pi) to interpret sensor inputs (ultrasonic, IR, cameras) and control actuators (motors, servos) accordingly. Advanced AI algorithms such as reinforcement learning and computer vision enable bots to adapt, predict opponent moves, and execute complex strategies autonomously.
What advancements in AI improve robot wrestling performance?
Key advancements include:
- Reinforcement Learning (RL): Allows bots to learn optimal strategies through trial and error, improving over time.
- Computer Vision (CV): Enables bots to visually track opponents and arena features, enhancing targeting and navigation.
- Behavior Trees and Finite State Machines: Provide structured decision-making frameworks for complex behaviors.
- Sensor Fusion: Combines data from multiple sensors for more accurate environmental perception.
- Deep Learning: Facilitates pattern recognition and predictive modeling, leading to emergent, unpredictable strategies.
These advancements collectively enhance a bot’s adaptability, speed of decision-making, and strategic depth.
Who are the leading designers in the official Robot Wrestling League?
The Robot Wrestling League™ features a diverse roster of talented engineers and teams worldwide. Notable figures include:
- Mark “The Maestro” Johnson: Renowned for robust mechanical designs and modular bots.
- Dr. Anya Sharma: Leading AI architect specializing in adaptive learning algorithms.
- Teams leveraging open-source collaboration: Many successful bots emerge from community-driven projects, emphasizing modularity and AI innovation.
The league fosters collaboration and competition, encouraging both veterans and newcomers to push boundaries.
What are the key features of successful wrestling bot designs?
Successful bots typically exhibit:
- Low center of gravity: For stability and resistance to flipping.
- High power-to-weight ratio: Ensuring speed and pushing force.
- Robust, modular chassis: For durability and easy repairs.
- Advanced sensor arrays: For precise opponent detection and arena awareness.
- Sophisticated AI: Capable of real-time decision-making and adaptation.
- Efficient power management: To sustain performance throughout matches.
Balancing these features is crucial for competitive success.
How do AI algorithms control robot battles in the Robot Wrestling League?
AI algorithms process continuous sensor data to assess the bot’s environment and opponent behavior. They use decision-making frameworks like behavior trees or reinforcement learning models to select actions—moving, attacking, defending—aimed at maximizing match success. Computer vision helps track opponents, while predictive models anticipate their moves. The AI dynamically adjusts strategies during the match, enabling autonomous control without human intervention.
What safety measures are used in robot wrestling competitions?
Safety is paramount. Measures include:
- Enclosed arenas with protective shields: To contain debris and protect spectators.
- Emergency stop systems: Allowing immediate shutdown of bots if needed.
- Pre-match inspections: Ensuring bots meet safety and design standards.
- Weight and power limits: Preventing excessively dangerous bots.
- Strict rules on weapon types and arena hazards: To minimize risk.
- Trained personnel and medical teams on-site: For rapid response.
These protocols ensure thrilling yet safe competitions.
How can beginners start building their own wrestling robots?
Beginners should:
- Start small: Use platforms like Arduino or Raspberry Pi.
- Learn basic electronics and programming: Tutorials and online courses help.
- Build simple bots: Focus on chassis, motors, and basic sensors.
- Experiment with simple AI: Implement finite state machines or basic obstacle avoidance.
- Leverage open-source resources: GitHub, forums, and community projects provide code and design inspiration.
- Participate in local or online competitions: Gain experience and feedback.
- Iterate and learn: Continuous testing and improvement are key.
Patience and persistence will pay off!
Additional FAQs
What role do digital twins play in wrestling bot development?
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical bots used for simulation and AI training. They allow developers to test strategies, optimize designs, and train AI in a risk-free environment, accelerating development and reducing physical wear.
How important is modularity in bot design?
Modularity enables quick repairs, easy upgrades, and experimentation with different components or weapons. It reduces downtime between matches and allows teams to adapt strategies rapidly.
Are humanoid wrestling bots feasible today?
While challenging, humanoid bots like Unitree H2 demonstrate advanced articulation and balance, making humanoid wrestling bots increasingly feasible. However, they require sophisticated AI and mechanical design to match the agility and dexterity of human wrestlers.
📚 Reference Links and Further Reading on Robotics and AI in Wrestling Bots
-
AI Robot Wrestling Open Source – opensource.com
https://opensource.com/article/23/2/ai-robot-wrestling-open-source -
Robotics and Artificial Intelligence in Wrestling Bots – M. Arkam C. on LinkedIn
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/arkam_wrestling-robots-ai-activity-7281612416851832832-STAt -
Robot Wrestling League™ Official Website
https://www.robotwrestling.org/ -
BattleBots Official Website
https://battlebots.com/ -
Robot Wars Wiki
https://robotwars.fandom.com/wiki/Robot_Wars -
Robot Operating System (ROS)
http://www.ros.org/ -
OpenCV – Open Source Computer Vision Library
https://opencv.org/ -
TensorFlow – Machine Learning Framework
https://www.tensorflow.org/ -
PyTorch – Deep Learning Framework
https://pytorch.org/ -
Gazebo Simulator
http://gazebosim.org/ -
Unity Robotics Hub
https://unity.com/blog/digital-twins-machinery-robotics-industry -
RoboCup Official Website
https://www.robocup.org/
Thanks for joining us on this thrilling exploration of robotics and AI in wrestling bots. Whether you’re a builder, a fan, or a curious newcomer, the arena is open, the bots are ready, and the future is bright. Let’s keep pushing the boundaries—one match at a time!