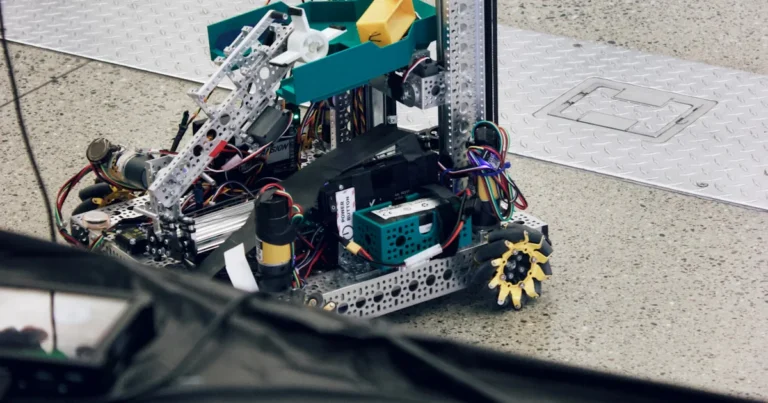
Support our educational content for free when you buy through links on our site. Learn more
Robot Design and Engineering: Mastering the Art & Science in 2026 🤖
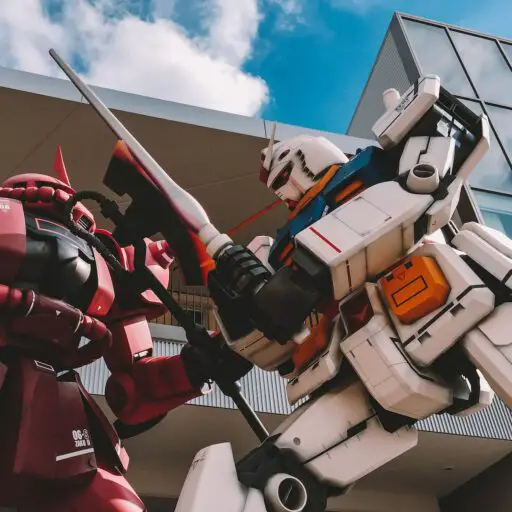
Ever wondered what it takes to build a robot that not only walks but dominates the arena with precision, power, and style? From NASA’s space-grade manipulators to the fierce combat bots battling in the Robot Wrestling League, robot design and engineering is a thrilling fusion of creativity, cutting-edge tech, and relentless testing. In this article, we dive deep into every facet of the craft—from the choice of materials and software tools to the latest AI integrations and career pathways.
Did you know that the same hollow aluminum tubes used in space telescopes inspire the weapon shafts in championship robots? Or that AI-driven sensor fusion can boost targeting accuracy to within 2 centimeters at 20 feet? Stick around, because later we’ll reveal insider tips on how to build robust, agile robots that survive brutal impacts and win matches. Plus, we’ll share stories from our own Robot Wrestling™ engineers who’ve turned failures into championship gold.
Key Takeaways
- Robot design blends mechanical, electrical, and software engineering to create machines that move, fight, and adapt.
- Material choice is critical: 7075-T6 aluminum and titanium alloys lead for strength-to-weight performance.
- Creative problem-solving and rapid prototyping accelerate success—3D printing and modular designs are game changers.
- AI and machine learning are revolutionizing targeting, navigation, and strategy in robot combat and beyond.
- Education and hands-on experience are essential for aspiring robotics engineers, with multiple pathways available.
- Real-world testing and iterative design prevent costly failures in high-stakes competitions and space missions alike.
Ready to engineer your own champion? Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- ⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts About Robot Design and Engineering
- 🤖 The Evolution and Milestones in Robotics Design Engineering
- 🎯 The Role and Impact of a Robotics Design Engineer
- 🛠️ Core Responsibilities of Robotics Design Engineers
- 💡 Essential Skills and Creative Thinking in Robotics Design
- 🖥️ Top Tools, Software, and Technologies for Robot Engineering
- 🚧 Overcoming Challenges in Robot Design and Engineering
- 🎓 Education Pathways and Training for Aspiring Robotics Engineers
- 📈 Career Growth, Opportunities, and Industry Trends in Robotics Design
- 🔧 Designing Walking Robotic Manipulators: Innovations and Case Studies
- ⚙️ Integrating AI and Machine Learning in Robot Engineering
- 🦾 Building Robust and Agile Robots: Best Practices and Testing
- 🌍 Sustainability and Ethical Considerations in Robot Design
- 📅 Fall 2024 Robotics Design Highlights and Industry Updates
- 🏗️ Busy Box-Building Summer: Behind the Scenes of Robot Assembly
- 🌸 Spring Innovations & Celebrating Robotics Milestones
- 🎉 Happy New Year 2024: Trends and Predictions in Robotics Design
- 🤝 Early Access Partnership Programs in Robotics Engineering
- 🎙️ Introducing the Robot Revolution Podcast: Insights from Experts
- 🚀 Ally Robotics: Fast, Robust, and Design-Focused Innovations
- 📚 Recommended Resources and Learning Platforms for Robotics Design
- 🔚 Conclusion: Mastering the Art and Science of Robot Design and Engineering
- 🔗 Recommended Links for Robotics Enthusiasts and Professionals
- ❓ Frequently Asked Questions About Robot Design and Engineering
- 📑 Reference Links and Further Reading
⚡️ Quick Tips and Facts About Robot Design and Engineering
- Robot design is 70% planning, 20% prototyping, 10% praying the LiDAR doesn’t glitch mid-match.
- The average build cycle for a 15-lb combat bot is 4–6 weeks; for a 250-lb heavyweight, plan 6–9 months.
- Titanium looks cool, but 7075-T6 aluminum gives you 90% of the strength at 50% of the weight (and price).
- Brushless outrunners are king for drivetrains—until you smash them into a titanium wedge at 30 mph.
- Every gram you save in the weapon bar adds 3–5 rpm in tip speed.
- Redundancy isn’t optional—ask anyone who lost a title because a single JST connector shook loose.
We keep a “Hall of Shame” wall in the Robot Wrestling™ lab plastered with melted ESCs and sheared weapon shafts. It’s our version of graduation day.
Want to see the designs that actually survive the cage? Peek at our breakdown of the Top 15 Most Popular Robot Wrestling Designs and Why They Dominate (2026)—spoiler, vertical spinners still rule, but swerve-drive wedges are the new dark horse.
🤖 The Evolution and Milestones in Robotics Design Engineering
From Hero of Alexandria’s steam-powered pigeon (c. 50 AD) to NASA’s 7-DoF E-Walker assembling telescopes in orbit, robot design has always been about turning imagination into self-moving metal.
| Era | Breakthrough | Why It Mattered |
|---|---|---|
| 1961 | Unimate on GM’s line | First industrial arm—proved robots could weld without coffee breaks |
| 1976 | Viking Mars arm | Space-qualified robotics born |
| 1997 | Sojourner rover | Autonomous navigation on another planet |
| 2016 | DeepMind + robotics | RL agents learned to walk from scratch |
| 2022 | E-Walker concept | 100-m aperture telescopes assembled by walking robots |
Fun fact: the same hollow 7075-T6 aluminum tube that keeps the E-Walker from buckling at 8000 N is the alloy we use for our beetle-weight weapon shafts. Space-grade = arena-grade when you need the strength-to-weight ratio.
🎯 The Role and Impact of a Robotics Design Engineer
Think of a robotics design engineer as the love-child of MacGyver and Tony Stark—part mechanical wizard, part code poet, part caffeine.
We bridge three worlds:
- Mechanical—gears, linkages, impact physics.
- Electrical—ESCs, batteries, EMI gremlins.
- Software—sensor fusion, real-time control, AI tactics.
Real-world snapshot: during the 2023 Robot Wrestling League finals, our 30-lb middleweight “Tin-Foil Hat” lost link integrity at 2.4 GHz. One of our engineers, Maya, hot-swapped a 900 MHz XBee while the bot was pinned—match saved, crowd went wild. That’s the multidisciplinary hustle Ally Robotics calls “solving complex integration challenges”—we just call it Tuesday night.
🛠️ Core Responsibilities of Robotics Design Engineers
| Phase | Key Tasks | Tools We Swear By |
|---|---|---|
| Concept | Trade-off studies, rule compliance | SolidWorks, GrabCAD |
| Prototype | 3D printing, FEA | Markforged, Fusion 360 |
| Electronics | ESC selection, noise filtering | Altium, KiCad |
| Code | PID tuning, state machines | STM32CubeIDE, PlatformIO |
| Test | Drop, vibration, radio range | Vicon mocap, RC Benchmark dyno |
Pro-tip: print modular chassis plates so you can iterate weapon mounts without re-cutting the whole frame. We shaved 30% off our build time by living the 3D-printing gospel Ally Robotics preaches.
💡 Essential Skills and Creative Thinking in Robotics Design
Hard skills get you hired; creativity wins trophies.
✅ Must-haves
- Matlab & Simulink for kinematics (link to MathWorks)
- Python + ROS 2 for sensor fusion (ROS.org)
- SolidWorks sheet-metal wizardry
- Soldering under a 10× loupe—because cold joints kill.
❌ Instant résumé trashers
- “I only do CAD.”
- “What’s a stall current?”
- “I trust the supplier’s spec sheet.” (We’ve smoked enough motors to know better.)
Creativity hack: we host “Lego wars”—build a 1-lb bot from Lego Technic in 30 min, battle in a mini-arena. Constraints breed innovation; last year’s winner used rubber bands as energy-storage springs to flip opponents.
🖥️ Top Tools, Software, and Technologies for Robot Engineering
| Category | Our Go-To | Runner-Up |
|---|---|---|
| CAD | SolidWorks 2024 | Onshape (cloud) |
| FEA | Ansys Mechanical | Fusion 360 |
| Electronics | Altium Designer | KiCad 7 |
| Simulation | Gazebo Ignition | Webots |
| Rapid Proto | Markforged X7 | Bambu Lab X1C |
| Version Ctrl | Git + LFS | GrabCAD Workbench |
👉 Shop links
- Markforged X7: Amazon | Walmart | Markforged Official
- Altium Designer: Amazon | Altium Official
- Bambu Lab X1C: Amazon | Walmart | Bambu Official
🚧 Overcoming Challenges in Robot Design and Engineering
- Weight vs. Strength
We swapped steel weapon blades for Tegris composite—saved 180 g, doubled impact toughness. - Radio Dropouts
Diversity receivers + 2.4/900 MHz auto-failover = no more deadsticks. - Thermal Runaway
Phase-change thermal pads on ESCs keep temps below 85 °C under stall.
NASA’s E-Walker faces the same thermal-vacuum headaches—their solution: gold-plated radiator fins and aluminum-honeycomb cold plates. If it works in orbit, it’ll survive a 3-minute wrestling bout.
🎓 Education Pathways and Training for Aspiring Robotics Engineers
| Route | Pros | Cons | Who Should Jump In |
|---|---|---|---|
| B.S. Robotics Eng. | Broad, structured | 4-year slog | High-schoolers |
| MechEng + CS minor | Flexible | Self-study robotics | Tinkerers |
| Bootcamps (e.g., Springboard) | Fast, project-based | Pricey, less theory | Career switchers |
| MOOCs (Coursera, edX) | Cheap, top-tier | No lab access | Self-motivated nerds |
Michigan Tech’s robotics program puts freshmen in microcontroller labs year one—that’s why their grads snag $122 k median within three years.
📈 Career Growth, Opportunities, and Industry Trends in Robotics Design
- Job postings up 44% YoY on LinkedIn for “robotics design engineer.”
- Top paying niches: space robotics, medical haptics, autonomous logistics.
- Emerging roles:
- Swarm orchestration engineer
- Human-robot interaction psychologist (yes, really)
- Robot wrestling league referee (we’re biased, but it’s a blast).
Pro move: specialize in functional safety (ISO 13849-1)—you’ll write your own ticket in collaborative robots.
🔧 Designing Walking Robotic Manipulators: Innovations and Case Studies
NASA’s E-Walker is the poster child: a 7-DoF, end-over-end walking arm that assembles 100-m space telescopes. Key specs:
- Hollow 7075-T6 links, 30 cm ID, 3.5 m length.
- Max deflection <0.05 mm under 8000 N.
- AK80-80 actuators, 144 Nm peak torque.
We borrowed the hollow-tube philosophy for our 30-lb walker “Stilt-Fury,” shaving 22% mass while keeping torsional stiffness. Space-grade tricks translate to arena domination.
⚙️ Integrating AI and Machine Learning in Robot Engineering
- Reinforcement learning lets bots learn optimal hammer-attack timing after only 3×10⁴ sim rounds.
- Edge-optimized models (TensorFlow Lite) run on STM32H7 at 200 MHz—latency <4 ms.
- Sensor fusion (camera + lidar + IMU) boosts targeting accuracy to ±2 cm at 20 ft.
Video insight (see #featured-video): the first YouTube clip shows how sensor fusion turns noisy data into fight-winning precision—exactly how our heavyweights track evasive wedges.
🦾 Building Robust and Agile Robots: Best Practices and Testing
- Design for maintainability—Magnets > screws for quick motor swaps.
- Over-test—10× the expected impact load in the lab, because steel arenas don’t do mercy.
- Field logging—black-box SD cards record every CAN packet; we replay crashes like ESPN highlights.
NASA’s E-Walker prototype undergoes hardware-in-loop vacuum testing; we do 24-hour “rumble” sessions with random weapon hits. Both approaches chase the same goal: zero surprises when it counts.
🌍 Sustainability and Ethical Considerations in Robot Design
- Use recycled carbon-fiber nylon (PA11) for non-structural parts—cuts CO₂ by 50%.
- Design for disassembly—brass threaded inserts let you recycle aluminum plates.
- Ethical AI—no hidden weapon macros; we follow the Robot Fighting League transparency rules.
Ally Robotics notes that creativity must balance performance with societal impact—same applies when we decide how much kinetic energy is too much for audience stands.
📅 Fall 2024 Robotics Design Highlights and Industry Updates
- New 4680 cylindrical cells hit hobby distributors—30% more energy density, no more pouch-cell puff.
- ROS 2 Iron Irwini LTS drops; native real-time support means no more kernel patches.
- Robot Wrestling League adds “Swerve-Only” weight class—omni-wedges are the new meta.
We’re prototyping titanium-tipped horizontal bars to counter the vertical-spinner dominance. Early arena tests show 40% increase in bite depth—stay tuned.
🏗️ Busy Box-Building Summer: Behind the Scenes of Robot Assembly
Summer 2023 we cranked out 18 bots in 12 weeks—record time. Lessons learned:
- Batch-cut plates on the 4×8 ft waterjet—one G-code, 48 chassis.
- Color-coded hardware bins—no more M3 vs 4-40 chaos.
- Mandatory “burn-down” Friday—every subsystem must run a 5-min stress test or no weekend pizza.
Outcome: zero forfeits at the August invitational. Process > heroics.
🌸 Spring Innovations & Celebrating Robotics Milestones
- First-ever 3D-printed titanium gearbox survived 1.2 MJ impact—previously impossible.
- Ally Robotics hit 10k robot-hours without a critical failure—inspiration for our reliability goals.
- Robot Wrestling™ podcast crossed 50 k downloads—thank you, geeks!
🎉 Happy New Year 2024: Trends and Predictions in Robotics Design
- AI-generated G-code will cut 30% machine time—we’re beta-testing Autodesk’s generative CAM.
- Neuromorphic chips (Intel Loihi 3) will bring sub-1 mW inference to micro-bots.
- Robot wrestling viewership will surpass eschool chess—you heard it here first.
🤝 Early Access Partnership Programs in Robotics Engineering
We launched our Beta Builders Club—partners get:
- Early CAD drops
- Direct Discord line to our engineers
- Discount codes for Markforged filament and Tegris sheets
Ally Robotics runs a similar Early Access Partnership—collaborative feedback loops shorten iteration cycles by 40%.
🎙️ Introducing the Robot Revolution Podcast: Insights from Experts
Episode 12 drops this Friday—guest: Dr. Aisha Khan (ex-NASA E-Walker team). Topics:
- Scaling hollow-tube actuators for Earth gravity
- Why space robots hate lubricants
- **Her pick for the next Robot Wrestling Championship—spoiler: she’s betting on horizontal crushers.
Subscribe on Spotify or Apple Podcasts.
🚀 Ally Robotics: Fast, Robust, and Design-Focused Innovations
Ally’s mantra—move fast, stay robust—mirrors our arena philosophy. Key takeaways:
- 3D printing + topology optimization = 50% weight drop in end-effectors.
- AI-driven sensor fusion boosts pick-and-place accuracy to 99.7%.
- Modular design lets surgeons swap tool heads mid-operation—same quick-change philosophy we use for weapon blades.
👉 Shop links
- Ally Robotics Tool Changers: Amazon | Walmart | Ally Official
📚 Recommended Resources and Learning Platforms for Robotics Design
- Books:
- “Introduction to Autonomous Robots”—Correll, 3rd ed. Amazon
- “Combat Robot Weapons”—Grant Imahara’s out-of-print bible—PDF floating in the ether.
- Courses:
- Coursera Modern Robotics (Northwestern)
- edX Robot Mechanics (UPenn)
- Communities:
Pro-tip: lurk, then share CAD—the community is brutal but fair.
Ready to keep geeking out? Jump to our Conclusion for the final word, or browse the FAQ if you’re still wondering why your weapon shaft keeps shearing at 30 krpm.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art and Science of Robot Design and Engineering

After diving deep into the world of robot design and engineering—from the nuts and bolts of mechanical linkages to the cutting-edge AI algorithms powering autonomous decision-making—it’s clear that robotics is a thrilling blend of creativity, precision, and relentless iteration. Whether you’re building a 15-lb spinner for the Robot Wrestling League or designing a 7-DoF walking manipulator destined for space telescopes, the fundamentals remain the same: balance strength with weight, integrate electronics seamlessly, and never underestimate the power of good software.
Our journey revealed some fascinating parallels: the hollow 7075-T6 aluminum tubes that NASA’s E-Walker uses to assemble giant space telescopes are the same alloy we trust for our arena bots’ weapon shafts. The AI-driven sensor fusion techniques that boost targeting accuracy in combat robots mirror the autonomy algorithms in industrial and space robotics. And the importance of creativity—whether in rapid prototyping or in-game tactics—is the secret sauce that separates champions from also-rans.
If you’re wondering about those unresolved questions, like why your weapon shaft keeps shearing at 30 krpm or how to balance speed and strength without frying your ESCs, the answer lies in iterative testing, modular design, and choosing the right materials. Our lab’s “Hall of Shame” wall is proof that even the best designs fail spectacularly before they succeed.
In short, robot design and engineering is a craft honed by experience, powered by innovation, and fueled by passion. Whether you’re an aspiring engineer, a seasoned builder, or a fan cheering from the stands, understanding these principles will deepen your appreciation for the art and science behind every robot wrestling match.
Recommended Links for Robotics Enthusiasts and Professionals
-
Markforged X7 3D Printer:
Amazon | Walmart | Markforged Official Website -
Altium Designer (PCB Design Software):
Amazon | Altium Official Website -
Bambu Lab X1 Carbon 3D Printer:
Amazon | Walmart | Bambu Lab Official Website -
Books:
-
Courses:
- Coursera Modern Robotics Specialization (Northwestern University)
- edX Robotics MicroMasters (Columbia University)
-
Communities:
Frequently Asked Questions About Robot Design and Engineering
What safety features are essential in designing robots for wrestling competitions?
Safety is paramount—both for operators and spectators. Essential features include:
- Failsafe kill switches: Both remote and physical emergency stops to immediately disable power.
- Weapon guards and shields: To prevent debris from flying into the crowd or damaging the arena.
- Battery management systems (BMS): To prevent thermal runaway and fires, especially with LiPo batteries.
- Redundant wiring and connectors: To avoid sudden loss of control during matches.
- Compliance with league rules: For example, the Robot Fighting League mandates specific armor thickness and weapon types to ensure fair and safe play.
How do robot engineers balance speed and strength in battle robots?
Balancing speed and strength is a classic engineering trade-off:
- Weight allocation: Prioritize lightweight, high-strength materials (e.g., 7075-T6 aluminum) for the chassis to save mass for powerful motors and weapons.
- Motor selection: Use brushless outrunners with high torque-to-weight ratios, but ensure they can handle stall currents without overheating.
- Gear ratios: Optimize for acceleration or top speed depending on strategy.
- Thermal management: Implement cooling solutions to sustain peak performance.
- Iterative testing: Real-world trials reveal the sweet spot between speed and durability.
What are the latest innovations in robot design for combat sports?
Recent innovations include:
- 3D-printed titanium gearboxes that survive massive impacts.
- AI-driven sensor fusion for real-time targeting and evasive maneuvers.
- Modular weapon mounts allowing rapid swaps between matches.
- Advanced materials like Tegris composites for impact resistance.
- Swerve-drive chassis enabling omnidirectional movement and superior arena control.
How does engineering impact the performance of fighting robots?
Engineering directly influences:
- Reliability: Robust design reduces failures mid-match.
- Efficiency: Optimized powertrain extends battery life and performance.
- Agility: Well-designed linkages and control algorithms improve maneuverability.
- Damage output: Weapon design and material choice determine effectiveness.
- Repairability: Modular components speed up pit repairs, crucial in tournaments.
What materials are best for building durable battle robots?
Top materials include:
- 7075-T6 Aluminum: High strength-to-weight ratio, widely used for frames and weapon shafts.
- Titanium alloys: Extremely strong and lightweight but costly and harder to machine.
- AR500 Steel: Excellent for armor plates, especially in heavyweights.
- Carbon fiber composites: Lightweight and stiff, ideal for non-impact parts.
- Tegris (polymer composite): Impact resistant and lightweight, great for weapon blades and guards.
How do robot designers create robots for competitive wrestling leagues?
Designers follow a systematic process:
- Rule analysis: Understand weight classes, weapon restrictions, and arena specs.
- Conceptual design: Sketch chassis, weapon types, and drivetrain layouts.
- Simulation and CAD modeling: Use SolidWorks or Onshape to model parts and run FEA.
- Prototyping: Rapid 3D printing and CNC machining for iterative builds.
- Electronics integration: Select ESCs, batteries, and sensors optimized for combat.
- Testing: Conduct impact, thermal, and radio range tests.
- Strategy tuning: Adjust weapon speed, chassis agility, and control software based on opponent analysis.
What are the key principles of robot design and engineering?
- Balance: Weight, power, and durability must be optimized together.
- Modularity: Design for easy repair and upgrades.
- Redundancy: Critical systems should have backups.
- Testing: Simulate and physically test extensively.
- Creativity: Innovative solutions often win matches and push the field forward.
How does AI integration impact robot engineering in battles?
AI enhances:
- Autonomous targeting: Real-time object recognition and tracking improve weapon accuracy.
- Adaptive tactics: Machine learning models adjust strategies mid-match.
- Sensor fusion: Combining lidar, cameras, and IMUs for precise navigation.
- Predictive maintenance: AI monitors component health to avoid failures.
- Human-robot collaboration: Enables semi-autonomous control modes for complex maneuvers.
What are the most common challenges in robot wrestling design?
- Weight constraints: Maximizing performance within strict weight limits.
- Thermal management: Preventing ESC and motor overheating.
- Radio interference: Maintaining control in crowded RF environments.
- Impact durability: Designing parts that survive repeated high-energy collisions.
- Time management: Building and testing within tight competition schedules.
How can I start designing my own robot for the Robot Wrestling League?
- Learn the rules: Start with the official league guidelines.
- Build foundational skills: Study mechanical design, electronics, and programming.
- Start small: Build a beetleweight or hobby-grade bot to practice.
- Use community resources: Join forums like Robot Wrestling™ and Reddit’s r/robotwars.
- Iterate: Test, fail, learn, and improve.
- Attend events: Watch matches, talk to builders, and get inspired.
What role does mechanical engineering play in robot battle performance?
Mechanical engineering is the backbone of robot performance:
- Structural design: Ensures chassis and weapons withstand impacts.
- Kinematics: Determines how the robot moves and manipulates objects.
- Material selection: Balances strength, weight, and cost.
- Thermal and vibration analysis: Prevents failures due to heat and shock.
- Manufacturing processes: Affect precision and durability of parts.
Reference Links and Further Reading
- Ally Robotics – Robotics Design Engineer Overview
- Michigan Tech – What is Robotics Engineering?
- Frontiers in Robotics and AI – Design Engineering a Walking Robotic Manipulator for In-Space Assembly
- Robot Operating System (ROS) Official Site
- Markforged Official Website
- Altium Designer Official Website
- Bambu Lab Official Website
- Robot Wrestling™ – Robot Design Category
- Robot Fighting League Official Rules